Overview
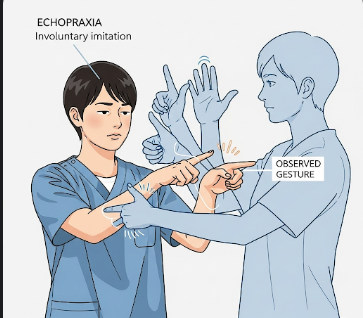
Echopraxia is a neurological or psychiatric symptom characterized by the involuntary imitation of another person’s movements or gestures. Unlike conscious mimicry, echopraxia occurs without intent or awareness, and can interfere with daily functioning and social interactions. It is often observed in neurodevelopmental disorders, movement disorders, or psychiatric conditions. In Korea, neurology, psychiatry, and rehabilitation clinics offer specialized assessment and management for echopraxia.
Highlights:
➤ Involuntary imitation of movements – Cannot control copying actions
➤ Associated with neurological or psychiatric conditions – Such as Tourette syndrome or schizophrenia
➤ Impacts social and functional behavior – May cause embarrassment or challenges in daily life
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Echopraxia is relatively uncommon but is frequently reported in Tourette syndrome, autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
➤ Age affected: Can be observed in children and adults depending on the underlying condition.
➤ Gender: Both men and women can be affected; some studies suggest higher prevalence in males with Tourette syndrome.
➤ Impact: Untreated echopraxia can lead to social difficulties, functional impairment, and reduced quality of life.
What is Echopraxia?
Echopraxia is defined as the uncontrolled repetition of another person’s physical movements or gestures, such as hand movements, facial expressions, or body postures. It can be classified as:
- Simple echopraxia: Repetition of single gestures or simple movements
- Complex echopraxia: Imitation of sequences of movements or more elaborate actions
- Associated echophenomena: Often appears with echolalia (repetition of speech) or other imitation behaviors
Highlights:
➤ Involuntary and automatic – Not consciously performed
➤ Varies in complexity – Simple gestures vs. complex sequences
➤ May co-occur with speech repetition or other mimicry behaviors
What Symptoms Are Related to Echopraxia?
➤ Involuntary imitation of movements – Arms, hands, facial expressions, or posture
➤ Repetition of sequences – Copying more complex actions of others
➤ Difficulty controlling imitation – Cannot prevent copying observed behaviors
➤ Social challenges: Embarrassment or misunderstandings in interactions
➤ Co-occurring symptoms: May include echolalia, tics, or compulsive behaviors
➤ Functional impairment: Interferes with learning, work, or social participation
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Tourette syndrome: Echopraxia is a type of complex motor tic
➤ Autism spectrum disorder (ASD): May present with imitation behaviors as part of repetitive or stereotyped actions
➤ Schizophrenia: Echopraxia may appear during catatonic states
➤ Neurodegenerative disorders: Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, or other basal ganglia disorders
➤ Brain injury or lesions: Damage to frontal lobes or mirror neuron systems
➤ Epilepsy or seizure disorders: Rarely, echopraxia can occur during ictal or postictal states
Highlights:
➣ Echopraxia can be neurological, psychiatric, or developmental in origin
➣ Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the underlying disorder and guide treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent involuntary imitation of movements – Interferes with daily life
➤ Associated motor tics, vocal tics, or behavioral changes
➤ Onset after brain injury or neurological illness
➤ Social or functional impairment – Difficulty in school, work, or social settings
➤ Co-occurring psychiatric symptoms – Catatonia, schizophrenia, or obsessive-compulsive behaviors
Highlights:
➣ Evaluation by a neurologist, psychiatrist, or pediatric neurologist in Korea is recommended
➣ Early assessment improves management of underlying conditions and functional outcomes
Care and Treatment
➤ Behavioral therapy: Cognitive-behavioral interventions to manage tics or imitation behaviors
➤ Occupational therapy: Improves control over motor movements and enhances daily functioning
➤ Speech therapy: If echopraxia co-occurs with echolalia or verbal imitation
➤ Medication: For underlying conditions such as Tourette syndrome, schizophrenia, or movement disorders (e.g., antipsychotics, alpha-agonists)
➤ Environmental modifications: Reduce triggers that elicit imitation behaviors
➤ Family and caregiver support: Guidance on managing symptoms and minimizing social stress
Highlights:
➣ Multidisciplinary approach improves functional independence, social skills, and quality of life
➣ Regular therapy and monitoring are essential for long-term management
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Neurology clinics: Diagnosis of tics, movement disorders, and neurological causes of echopraxia
➤ Psychiatry clinics: Management of catatonia, schizophrenia, and psychiatric comorbidities
➤ Pediatric neurology centers: Specialized care for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Neuroimaging: MRI or CT scans to detect structural brain abnormalities
➤ Neurocognitive assessments: Identify deficits in motor control or executive function
➤ Medication management: Tailored pharmacological treatment for tics or psychiatric disorders
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Ongoing monitoring of motor behaviors, social functioning, and medication effects
➤ Collaboration among therapists, educators, and families for consistent reinforcement
➤ Holistic care in Korea integrates neurology, psychiatry, occupational therapy, and rehabilitation services
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide comprehensive, multidisciplinary care for echopraxia
➣ Early and targeted interventions improve motor control, social interaction, and daily functioning