Overview
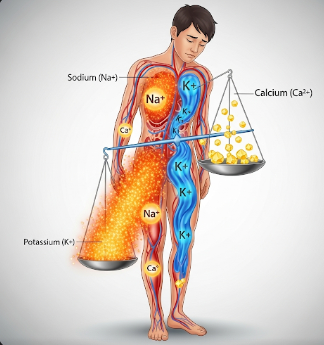
Electrolyte imbalance occurs when the levels of electrolytes in the body are either too high or too low, disrupting normal physiological functions. Electrolytes are minerals such as sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and chloride, which are essential for nerve function, muscle contraction, hydration, and acid-base balance. Imbalances can result from dietary deficiencies, medical conditions, medications, or excessive fluid loss. In Korea, internal medicine and nephrology clinics provide comprehensive assessment and treatment for electrolyte disturbances to prevent severe complications.
Highlights:
➤ Critical minerals in the body – Sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride
➤ Essential for organ function – Heart, muscles, nerves, and kidneys
➤ Imbalance can be life-threatening – Requires prompt diagnosis and management
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Electrolyte imbalances are common in hospitalized patients and individuals with chronic illnesses such as kidney disease or heart failure.
➤ Age affected: Can affect all age groups, from children to elderly adults.
➤ Causes: Dehydration, kidney disorders, endocrine issues, medication side effects, or malnutrition.
➤ Impact: Untreated imbalances can cause cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, muscle weakness, or organ failure.
What is Electrolyte Imbalance?
Electrolyte imbalance is the disruption of normal concentrations of electrolytes in the blood or tissues, leading to impaired physiological processes. It can manifest as:
- Hyponatremia: Low sodium
- Hypernatremia: High sodium
- Hypokalemia: Low potassium
- Hyperkalemia: High potassium
- Hypocalcemia / Hypercalcemia: Low or high calcium
- Hypomagnesemia / Hypermagnesemia: Low or high magnesium
Highlights:
➤ Affects multiple organ systems – Heart, muscles, nerves, and kidneys
➤ May be acute or chronic – Depending on cause and severity
➤ Symptoms vary – From mild fatigue to severe cardiac complications
What Symptoms Are Related to Electrolyte Imbalance?
➤ Muscle weakness or cramps – Especially with potassium or calcium disturbances
➤ Fatigue or lethargy – Generalized feeling of weakness
➤ Confusion or altered mental status – Severe sodium or calcium imbalance
➤ Irregular heartbeat or palpitations – Potassium and magnesium abnormalities
➤ Nausea or vomiting – Often associated with fluid and electrolyte loss
➤ Seizures or tremors – Severe electrolyte disturbances
➤ Thirst and dehydration – Particularly in sodium imbalance
➤ Swelling or edema – Fluid retention linked with electrolyte disorders
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Dehydration: From vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, or inadequate fluid intake
➤ Kidney disorders: Impaired electrolyte regulation in chronic kidney disease or acute kidney injury
➤ Medications: Diuretics, corticosteroids, or chemotherapy drugs affecting electrolyte levels
➤ Endocrine disorders: Diabetes, adrenal insufficiency, or thyroid imbalances
➤ Malnutrition or dietary deficiencies: Insufficient intake of essential minerals
➤ Heart or liver disease: Fluid and electrolyte regulation disruption
➤ Excessive fluid replacement: Overcorrection with IV fluids can cause imbalances
Highlights:
➣ Electrolyte imbalances can result from loss, excess, or redistribution of minerals
➣ Accurate diagnosis is essential for safe and effective correction
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent symptoms – Weakness, confusion, or palpitations
➤ Severe or sudden changes – Especially in potassium, calcium, or sodium levels
➤ Associated medical conditions – Kidney disease, heart failure, or endocrine disorders
➤ Following vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive sweating – Risk of acute imbalance
➤ During medication use – Diuretics or other drugs affecting electrolytes
Highlights:
➣ Early evaluation at a Korean internal medicine or nephrology clinic is critical
➣ Prompt intervention prevents life-threatening complications like arrhythmias or seizures
Care and Treatment
➤ Laboratory testing: Blood tests to measure sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and chloride levels
➤ Fluid replacement: Oral or IV hydration to correct dehydration-related imbalances
➤ Electrolyte supplementation: Potassium, calcium, or magnesium supplementation as needed
➤ Medication adjustment: Modifying or discontinuing drugs contributing to imbalance
➤ Dietary modifications: Ensuring adequate intake of essential minerals
➤ Monitoring: Continuous evaluation of electrolyte levels, especially in hospitalized or high-risk patients
Highlights:
➣ Treatment depends on type, severity, and underlying cause
➣ Multidisciplinary care ensures safe correction and prevention of recurrence
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Nephrology clinics: Comprehensive assessment for electrolyte disturbances
➤ Internal medicine departments: Management of imbalances due to chronic illness or acute illness
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Corrective supplementation, diuretic adjustment, or endocrine management
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Intravenous electrolyte replacement: Rapid correction for severe imbalances
➤ Dialysis: For severe kidney failure causing persistent imbalances
➤ Continuous monitoring: In ICUs for critical patients with dynamic electrolyte shifts
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Ongoing lab monitoring and dietary counseling
➤ Education on hydration, nutrition, and medication adherence
➤ Integration of multidisciplinary care including nephrologists, dietitians, and cardiologists
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide state-of-the-art diagnostics and treatment for electrolyte imbalances
➣ Early intervention improves organ function, symptom relief, and overall patient safety