Overview
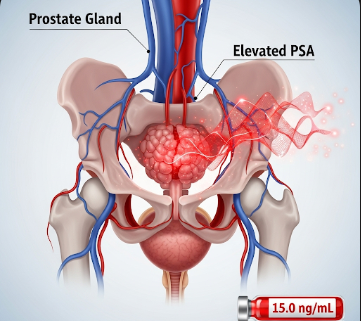
Elevated PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) level refers to higher-than-normal concentrations of PSA in the blood, which can be an indicator of prostate health issues. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland, and its levels can increase due to prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or prostatitis. Elevated PSA does not automatically indicate cancer but serves as an important screening and monitoring tool. In Korea, urology clinics and hospitals offer specialized testing, follow-up, and treatment for men with elevated PSA levels to ensure early detection and effective management of prostate conditions.
Highlights:
➤ Blood marker for prostate health – PSA is produced by prostate cells
➤ May indicate benign or malignant conditions – Not diagnostic of cancer alone
➤ Early detection is key – Helps prevent progression of prostate diseases
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Elevated PSA is common in men over 50, but younger men may also show elevation due to inflammation or infection.
➤ Age affected: Risk increases with age, particularly after 50 years.
➤ Gender: Exclusively affects men, as the prostate is a male organ.
➤ Impact: Persistent elevation can indicate prostate cancer, BPH, or prostatitis, and may require further evaluation to guide treatment.
What is Elevated PSA Level?
PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) is a protein secreted by prostate cells into the semen, with a small amount normally entering the bloodstream. Elevated PSA occurs when more PSA enters the blood, which can result from:
- Prostate cancer: Malignant cells increase PSA production
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): Enlarged prostate releases more PSA
- Prostatitis: Inflammation or infection of the prostate
- Procedures or trauma: Catheterization, biopsy, or recent ejaculation
Highlights:
➤ Marker of prostate activity, not a definitive diagnosis
➤ Can be influenced by age, infection, or procedures
➤ Requires follow-up testing for accurate interpretation
What Symptoms Are Related to Elevated PSA?
It is important to note that elevated PSA may occur without symptoms, but related prostate issues can produce:
➤ Frequent urination – Especially at night (nocturia)
➤ Difficulty starting or stopping urination – Weak urinary stream
➤ Painful urination or burning sensation – Common in prostatitis
➤ Blood in urine or semen – Hematuria or hematospermia
➤ Pelvic or lower back pain – Sometimes associated with advanced prostate disease
➤ Urinary retention or incomplete emptying – Due to prostate enlargement
Highlights:
➣ PSA elevation may be asymptomatic, but symptoms warrant prompt evaluation
➣ Symptoms help clinicians differentiate BPH, infection, or cancer
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Prostate cancer: Malignant growth increases PSA levels, sometimes significantly
➤ Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): Non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate
➤ Prostatitis: Bacterial or non-bacterial inflammation
➤ Recent prostate procedures or trauma: Biopsy, catheterization, or surgery
➤ Age-related changes: PSA naturally rises with age
➤ Urinary tract infection or ejaculation: Temporary elevation due to irritation or activity
Highlights:
➣ Elevated PSA is not diagnostic alone – Requires imaging, biopsy, or repeat testing
➣ Understanding the cause is essential for appropriate management
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent PSA elevation – Detected during routine screening
➤ Symptoms of urinary difficulty, pain, or blood in urine/semen
➤ Family history of prostate cancer – Increases risk significantly
➤ Previous abnormal PSA tests – Requires follow-up evaluation
➤ Age over 50 or high-risk ethnicity – Early screening recommended
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean urologist ensures timely investigation
➣ Preventive screening and monitoring reduce risk of advanced prostate cancer
Care and Treatment
➤ Repeat PSA testing: Confirms persistent elevation or trends over time
➤ Digital rectal exam (DRE): Clinical assessment of prostate size, nodules, or irregularities
➤ Imaging studies: Ultrasound, MRI, or multiparametric MRI to evaluate prostate structure
➤ Biopsy: Recommended if PSA elevation persists or imaging shows abnormalities
➤ Treatment based on cause:
- BPH: Medications (alpha-blockers, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors) or minimally invasive procedures
- Prostatitis: Antibiotics or anti-inflammatory therapy
- Prostate cancer: Surgery, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, or active surveillance
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of prostate irritants
Highlights:
➣ Management depends on underlying cause, PSA levels, and patient risk factors
➣ Regular monitoring ensures early detection and prevention of disease progression
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Urology clinics: Comprehensive PSA evaluation, DRE, and laboratory testing
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Medications for BPH, prostatitis, or early intervention strategies
➤ Cancer management: Radical prostatectomy, radiotherapy, or hormonal therapy
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Multiparametric MRI: High-resolution imaging to detect prostate lesions
➤ Targeted biopsy: Guided by imaging for accurate diagnosis
➤ Minimally invasive BPH procedures: Laser therapy or transurethral resection
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular PSA monitoring and imaging as needed
➤ Lifestyle counseling to support prostate health
➤ Integration of urology, oncology, and primary care specialists for comprehensive care
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics offer state-of-the-art diagnostics, targeted interventions, and individualized monitoring
➣ Early evaluation and treatment improve prognosis, symptom control, and quality of life