Overview
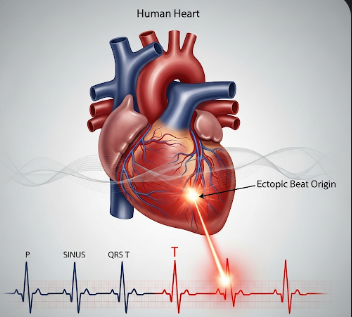
Ectopic beats, also known as premature heartbeats, are extra or irregular heartbeats originating from the heart’s atria (PACs) or ventricles (PVCs). These abnormal beats disrupt the normal rhythm of the heart, often causing a fluttering, skipped beat, or pounding sensation in the chest. While occasional ectopic beats are common and usually benign, frequent or symptomatic ectopy may indicate underlying cardiac conditions. In Korea, cardiology clinics and hospitals provide detailed evaluation, including electrocardiography (ECG), Holter monitoring, and advanced imaging, to detect, assess, and manage ectopic beats effectively.
Highlights:
➤ Irregular, extra heartbeats – Can occur in healthy individuals or patients with heart disease
➤ May cause palpitations, fluttering, or skipped beats
➤ Requires evaluation if frequent, symptomatic, or associated with underlying heart conditions
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Ectopic beats are common; occasional PACs or PVCs occur in up to 70% of healthy adults
➤ Age affected: Can occur at any age; prevalence increases with age and cardiovascular risk factors
➤ Gender: Slightly higher incidence in males, especially for PVCs
➤ Impact: Most are benign; frequent or symptomatic ectopic beats may lead to anxiety, reduced quality of life, or rarely, arrhythmias
➤ Prognosis: Generally excellent in healthy individuals; underlying heart disease may affect prognosis
What are Ectopic Beats?
Ectopic beats are premature contractions of the heart that occur outside the normal heartbeat sequence. Types include:
- Premature atrial contractions (PACs): Early beats originating in the atria
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs): Early beats originating in the ventricles, often producing stronger palpitations
- Multifocal or frequent ectopy: May indicate increased cardiac irritability or underlying pathology
Key characteristics:
- Fluttering, skipped, or pounding sensations in the chest
- Occasional dizziness or shortness of breath in some cases
- Usually asymptomatic and discovered on ECG
Highlights:
➤ Extra heartbeats originating in atria or ventricles
➤ Can be benign or indicate underlying cardiac disease
➤ ECG and Holter monitoring are key diagnostic tools
What Symptoms Are Related to Ectopic Beats?
➤ Palpitations or skipped beats – Primary and most common symptom
➤ Fluttering or pounding sensation in the chest
➤ Mild dizziness or lightheadedness – Due to transient reduction in cardiac output
➤ Shortness of breath – Usually during exertion or in patients with heart disease
➤ Fatigue or decreased exercise tolerance – In frequent ectopy
➤ Chest discomfort – Rare, but may occur in frequent or prolonged episodes
➤ Anxiety or stress – Secondary to awareness of irregular heartbeat
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms may be occasional or persistent
➣ Symptomatic or frequent ectopy requires medical evaluation
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Lifestyle triggers: Stress, caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, and excessive exercise
➤ Electrolyte imbalances: Low potassium, magnesium, or calcium levels
➤ Medications: Decongestants, stimulants, or certain asthma medications
➤ Heart conditions: Hypertension, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, ischemic heart disease
➤ Structural heart disease: Valve disorders, congenital heart defects, prior myocardial infarction
➤ Other medical conditions: Hyperthyroidism, anemia, or systemic infection
➤ Idiopathic: Many ectopic beats occur in otherwise healthy hearts without identifiable cause
Highlights:
➣ Causes range from benign triggers to serious cardiac disease
➣ Identifying triggers and underlying conditions is critical for effective management
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Frequent or worsening palpitations – Occurring several times per day
➤ Associated dizziness, fainting, or chest pain – Suggests significant arrhythmia
➤ History of heart disease or risk factors – Hypertension, coronary artery disease, or heart failure
➤ Abnormal findings on ECG or Holter monitoring
➤ New or unexplained fatigue or exercise intolerance
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean cardiologist ensures correct diagnosis and risk stratification
➣ Timely evaluation prevents complications such as sustained arrhythmias or cardiac events
Care and Treatment
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Reduce caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine; manage stress and sleep
➤ Electrolyte correction: Address deficiencies in potassium, magnesium, or calcium
➤ Medication review: Adjust or discontinue stimulants or arrhythmogenic drugs
➤ Beta-blockers or antiarrhythmic medications: Prescribed for symptomatic or frequent ectopy
➤ Catheter ablation: Considered in severe, refractory, or high-risk ventricular ectopy
➤ Monitoring: ECG, Holter, or event monitoring to track frequency and pattern
Highlights:
➣ Most ectopic beats in healthy individuals are benign and self-limiting
➣ Symptomatic or frequent ectopy may require medication or interventional treatment
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Cardiology clinics: ECG, Holter monitoring, echocardiography, and blood tests
➤ Prescription medications: Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or antiarrhythmics
➤ Lifestyle counseling: Stress management, dietary modification, and exercise recommendations
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Catheter ablation: Minimally invasive procedure to eliminate abnormal cardiac foci
➤ Implantable devices: In rare cases, pacemakers or defibrillators for high-risk arrhythmias
➤ Follow-up care: Regular cardiac evaluation to monitor recurrence or progression
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Patient education on symptom recognition and lifestyle triggers
➤ Continuous monitoring for arrhythmia recurrence or underlying heart disease
➤ Multidisciplinary care for patients with complex cardiac comorbidities
Highlights:
➣ Korean cardiology centers provide advanced diagnostics, targeted therapy, and long-term monitoring
➣ Early intervention ensures symptom relief, risk reduction, and improved quality of life