Overview
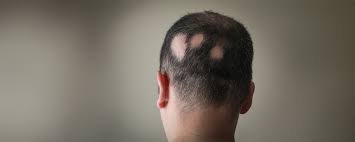
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes sudden, unpredictable hair loss, typically in round patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. Though not life-threatening, it can cause significant emotional distress and impact self-esteem. In South Korea, advanced dermatological care and alternative therapies are available for managing this condition.
What is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. The follicles are not permanently damaged, so regrowth is possible, especially with treatment. The condition can affect people of any age or gender, though it often begins before age 30.
There are several types:
- Alopecia areata: Patchy hair loss on the scalp or body
- Alopecia totalis: Complete scalp hair loss
- Alopecia universalis: Total loss of hair on scalp and body
Symptoms
- Sudden hair loss in small, round patches
- Tingling, burning, or itching in affected areas
- Brittle or pitted fingernails or toenails
- Hair loss on eyebrows, eyelashes, or beard
- Regrowth may occur, often white or fine at first
In some cases, hair loss may come and go, or progress to more extensive loss.
Causes
The exact cause is unknown, but it’s believed to be an autoimmune response. Contributing factors may include:
- Genetics (family history)
- Other autoimmune diseases (e.g., thyroid disorders, vitiligo)
- Stress or trauma (emotional or physical)
- Viral infections
Risk Factors
- Family history of alopecia areata or autoimmune conditions
- History of autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Younger age (often starts in childhood or adolescence)
- Stressful life events
- Personal or family history of allergies or asthma
Complications
- Emotional and psychological impact, including anxiety, depression, or social withdrawal
- Permanent hair loss (in rare, severe cases)
- Nail abnormalities
- Increased risk of other autoimmune conditions
Prevention
Alopecia areata cannot be fully prevented, but you can reduce flare-ups or slow progression through:
- Managing stress through mindfulness or therapy
- Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet
- Avoiding chemical damage (harsh treatments or dyes)
- Regular medical checkups if you have autoimmune conditions
- Early treatment when symptoms begin
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers cutting-edge treatments for alopecia areata through a combination of medical dermatology and holistic approaches:
1. Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation
- Minoxidil (Rogaine) for promoting hair regrowth
- Anthralin or diphencyprone (DPCP) to stimulate regrowth
2. Intralesional Injections
- Corticosteroid injections directly into bald patches to suppress immune response
3. Oral Medications
- Systemic corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressants (e.g., methotrexate, cyclosporine)
- JAK inhibitors (e.g., baricitinib), available in advanced dermatology clinics
4. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
- UVB or PUVA therapy, used in combination with medication to stimulate follicles
5. Korean Traditional Medicine (Hanbang)
- Herbal scalp tonics
- Acupuncture for immune balance and blood flow
- Stress reduction therapies (e.g., cupping, moxibustion)
Specialized clinics like CHA Bundang Medical Center or Samsung Medical Center in Seoul offer integrative approaches combining Western and Eastern medicine.
6. Supportive Therapies
- Wig and hairpiece fitting services
- Psychological counseling
- Patient support groups