Overview
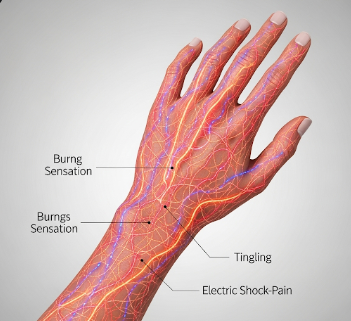
Dysesthesia is a neurological condition characterized by abnormal, often unpleasant sensations on the skin or other parts of the body. Patients may describe it as burning, tingling, electric shocks, or itching, even when there is no external stimulus. Dysesthesia can significantly affect daily comfort, sleep, and quality of life. In Korea, leading neurology and pain management clinics provide advanced evaluation and treatment for patients suffering from dysesthesia.
Highlights:
➤ Neurological condition – Involves peripheral or central nerves
➤ Sensory disturbance – Can range from mild tingling to severe pain
➤ Chronic impact – May persist if underlying causes are untreated
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Dysesthesia occurs in various neurological disorders, including diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and peripheral neuropathy.
➤ Age group affected: Adults are most commonly affected, especially those with chronic medical conditions; however, it can occur at any age.
➤ Gender: Both men and women are susceptible.
➤ Impact: Chronic discomfort may lead to sleep disturbance, anxiety, and reduced mobility.
What is Dysesthesia?
Dysesthesia refers to unpleasant, abnormal sensations that occur spontaneously or in response to a stimulus that is normally not painful. Unlike normal tingling or mild numbness, dysesthesia sensations are often distressing and can include:
Highlights:
➤ Burning or stinging sensations
➤ Electric shock-like feelings
➤ Tingling or prickling (pins and needles)
➤ Itching without rash
It may affect localized areas, such as hands or feet, or be widespread depending on the underlying cause.
What Symptoms Are Related to Dysesthesia?
➤ Paresthesia: Mild tingling or numbness often accompanies dysesthesia.
➤ Pain sensations: Can range from mild discomfort to severe burning pain.
➤ Hypersensitivity: Even light touch or clothing can provoke discomfort.
➤ Muscle weakness or coordination issues: Sometimes associated with nerve disorders.
➤ Sleep disturbance: Persistent discomfort may interfere with rest.
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Peripheral neuropathy: Diabetes, chemotherapy, or vitamin deficiencies can damage peripheral nerves.
➤ Multiple sclerosis (MS): Demyelination of nerves can trigger dysesthetic sensations.
➤ Spinal cord injuries: Damage to central nerves can result in abnormal sensations below the injury site.
➤ Nerve compression: Herniated discs or carpal tunnel syndrome can contribute to dysesthesia.
➤ Post-herpetic neuralgia: Nerve pain following shingles infection.
➤ Medications or toxins: Certain drugs or exposure to heavy metals may cause nerve irritation.
Highlights:
➣ Dysesthesia often arises from nerve damage or dysfunction, either peripheral or central.
➣ Identifying the underlying cause is essential for effective management.
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent or worsening sensations: Especially if they interfere with daily life
➤ Severe pain or burning: May indicate nerve injury or progressive neuropathy
➤ Sudden onset: Could signal acute nerve damage or underlying neurological disorder
➤ Associated weakness or numbness: Requires urgent evaluation to prevent complications
➤ Unresponsive to home care: Persistent dysesthesia needs professional assessment
Highlights:
➣ Neurologists in Korea can perform nerve conduction studies, imaging, and laboratory tests to pinpoint causes.
➣ Early intervention improves outcomes and prevents progression of nerve damage.
Care and Treatment
➤ Medications:
• Anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin or pregabalin) for nerve pain
• Antidepressants (e.g., duloxetine, amitriptyline) for neuropathic pain management
➤ Topical therapies: Creams or patches containing lidocaine or capsaicin to reduce localized pain
➤ Physical therapy: Gentle exercises can improve mobility and reduce discomfort
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining blood sugar in diabetics, avoiding neurotoxic substances
➤ Complementary therapies: Acupuncture or nerve stimulation therapies may provide relief
Highlights:
➣ Combination therapy is often most effective
➣ Consistent management can reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Neurology clinics: Offer comprehensive evaluation and management of dysesthesia
➤ Pharmacological management: Prescription medications tailored to type and severity of symptoms
➤ Specialized pain clinics: Provide nerve blocks, spinal injections, or advanced analgesic therapies
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): Helps modulate abnormal nerve signals
➤ Laser therapy or neuro-modulation: Available in specialized centers for chronic neuropathic pain
➤ Rehabilitation programs: Integrated care including physical therapy and counseling
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular follow-ups ensure proper medication adjustments and monitor nerve function
➤ Patient education on lifestyle, ergonomics, and self-care reduces recurrence
➤ Holistic approaches in Korea combine neurology, pain management, and physical rehabilitation
Highlights:
➣ Korea provides state-of-the-art clinics with multidisciplinary care
➣ Treatments are tailored to individual nerve pathology and severity