Overview
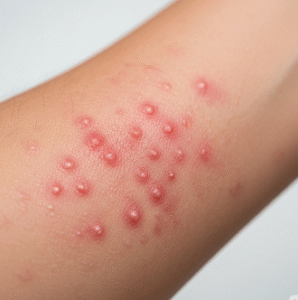
Chills are the sensation of coldness accompanied by shivering, often occurring when the body is fighting an infection, exposed to cold environments, or experiencing systemic stress. Chills can range from mild discomfort to severe shaking and may occur with or without fever.
In South Korea, general practitioners and hospitals evaluate chills as part of comprehensive diagnostic assessments, including infection screening, blood tests, and imaging, to determine underlying causes and guide effective treatment.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Chills often accompany fever, flu, infections, or inflammatory conditions.
➡️ They can be a protective physiological response, helping the body raise core temperature to fight pathogens.
➡️ Persistent or severe chills may indicate serious medical conditions, including sepsis or systemic infections.
➡️ Chills may also occur without fever, due to exposure to cold, hypoglycemia, anemia, or thyroid disorders.
➡️ South Korea’s healthcare system provides advanced diagnostic and treatment options for both common and severe causes of chills.
What is Chills?
Chills are an involuntary bodily response to perceived cold or internal infection, characterized by:
- Shivering and trembling, often involuntary
- Piloerection (goosebumps) on the skin
- Feeling cold despite normal or elevated body temperature
- Often associated with fever or systemic illness
Key Characteristics:
- Can be acute or recurrent, depending on the underlying cause
- Often accompanied by sweating, fatigue, or weakness
- Usually resolves once the underlying condition is treated
What Symptoms are Related to Chills?
Chills can appear alongside a variety of other symptoms, including:
- Fever or elevated body temperature
- Sweating or clammy skin
- Muscle aches or body weakness
- Headache or dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting in infection-related cases
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations in systemic illness
Highlights:
➡️ Chills are often the first sign of infection or inflammation in the body.
➡️ Combination with fever, malaise, or localized pain helps guide diagnosis.
➡️ Persistent chills without fever may indicate endocrine or hematologic disorders.
What Causes / Possible Causes of Chills?
Highlights:
➡️ Infections:
- Viral infections like influenza or COVID-19
- Bacterial infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, or sepsis
➡️ Cold Exposure: Hypothermia or prolonged exposure to low temperatures.
➡️ Systemic Disorders:
- Anemia or blood loss
- Hypothyroidism or other endocrine dysfunctions
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
➡️ Medications: Certain drugs can trigger chills as a side effect.
➡️ Other Causes: Post-vaccination reactions, autoimmune conditions, or severe inflammatory responses.
➡️ Mechanism: Chills occur when the body’s thermoregulatory center in the hypothalamus triggers muscle contractions to raise core temperature and fight perceived threats.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If chills are persistent, severe, or accompanied by high fever.
➡️ If chills occur with chest pain, difficulty breathing, or confusion, as these may indicate serious infections or systemic issues.
➡️ If there is blood in urine, stool, or unusual bleeding, consult a doctor immediately.
➡️ For recurring chills without obvious cause, evaluation for anemia, thyroid disorders, or metabolic conditions is recommended.
➡️ Early consultation ensures proper diagnosis and timely treatment, preventing complications such as sepsis or organ dysfunction.
Care and Treatment
Treatment of chills depends on the underlying cause:
Highlights:
➡️ Symptomatic Relief:
- Warm clothing and blankets
- Maintaining ambient warmth
- Hydration to support body temperature regulation
➡️ Medication:
- Antipyretics (paracetamol/acetaminophen) for fever-related chills
- Antibiotics or antivirals for infection-based causes
- Hormone or metabolic therapy for thyroid or blood sugar disorders
➡️ Lifestyle Measures:
- Proper nutrition to prevent hypoglycemia or anemia
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to cold environments
- Rest to support immune system function
➡️ Hospital Care: In severe cases, intravenous fluids, oxygen therapy, or intensive monitoring may be necessary.
➡️ Follow-Up Monitoring: Ensures symptoms resolve and underlying causes are fully addressed.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced care for patients experiencing chills, including:
Highlights:
➡️ General Practice & Internal Medicine Clinics: Comprehensive evaluation of infection, metabolic, or systemic causes.
➡️ Hospital-Based Diagnostic Services: Blood tests, imaging, and cultures to identify underlying illness.
➡️ Infectious Disease Clinics: Management of viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections causing chills.
➡️ Endocrinology & Metabolic Care: Treatment for thyroid disorders, hypoglycemia, or anemia-related chills.
➡️ Multidisciplinary Approach: Coordination among internists, infectious disease specialists, and endocrinologists for holistic care.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Multilingual consultations, rapid diagnostics, and treatment for international patients visiting Korea.