Overview
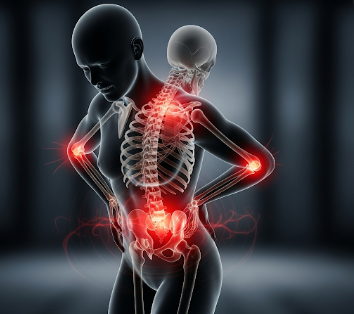
Bone pain is a type of discomfort or aching that originates from the bones themselves or the surrounding structures. Unlike muscle or joint pain, bone pain is often deep, dull, or throbbing, and may indicate injury, infection, metabolic issues, or systemic disease. Early recognition is essential, as persistent bone pain can signal conditions that require diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.
In South Korea, orthopedic clinics, rheumatology centers, and specialized hospitals provide comprehensive evaluation, imaging, and treatment options for patients experiencing bone pain, ensuring both relief and long-term skeletal health.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Bone pain can affect any bone in the body, from the skull to the limbs.
➡️ It may be localized or diffuse, acute or chronic.
➡️ Common causes include fractures, osteoporosis, arthritis, infections, and cancer.
➡️ Systemic conditions, such as vitamin D deficiency or metabolic disorders, can also contribute.
➡️ South Korea offers advanced diagnostic imaging, lab tests, and treatment plans tailored to the underlying cause.
What is Bone Pain?
Bone pain is discomfort originating from inside or around the bone.
Characteristics include:
- Deep, dull, or throbbing sensation in the affected bone
- Pain may worsen at night or with activity
- Often accompanied by swelling, tenderness, or reduced mobility if the surrounding joints are involved
- May be localized to a specific bone or diffuse throughout the skeleton
- Can indicate trauma, disease, or metabolic abnormalities
Bone pain is distinct from joint or muscle pain, though it may coexist with other musculoskeletal symptoms.
What Symptoms are Related to Bone Pain?
Symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause:
- Persistent aching or tenderness in the bone
- Swelling or redness over affected area in case of infection or trauma
- Fractures or deformities in severe cases
- Fatigue, fever, or systemic symptoms if caused by infection or malignancy
- Limited mobility or difficulty bearing weight
- Night pain often indicates more serious conditions such as tumors or metabolic bone disease
Highlights:
➡️ Bone pain may be worse at rest or during activity, depending on the cause.
➡️ Associated systemic symptoms help differentiate between localized injury and systemic disease.
What Causes / Possible Causes of Bone Pain?
Highlights:
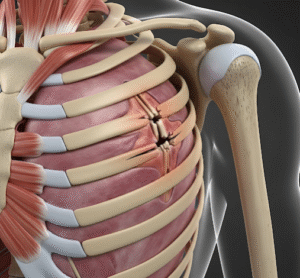
➡️ Trauma and Fractures: Accidents, falls, or repetitive stress injuries causing direct damage.
➡️ Osteoporosis: Weakening of bones due to calcium or vitamin D deficiency, leading to fractures and chronic pain.
➡️ Arthritis and Joint Disorders: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can cause referred bone pain.
➡️ Infections (Osteomyelitis): Bacterial or viral infections affecting bone tissue.
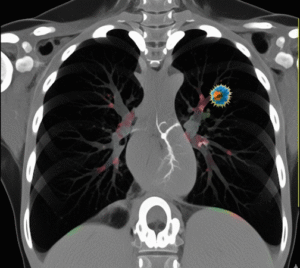
➡️ Cancer: Primary bone tumors or metastases can present with persistent bone pain.
➡️ Metabolic or Endocrine Disorders:
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Paget’s disease of bone
➡️ Hematologic Disorders: Sickle cell disease or leukemia can cause bone pain.
➡️ Other Causes: Bone marrow disorders, chronic kidney disease, or prolonged immobility.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If bone pain is persistent or severe, and does not improve with rest or over-the-counter medications.
➡️ If accompanied by swelling, redness, or warmth, which may indicate infection or inflammation.
➡️ If associated with fever, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss, suggesting systemic disease or malignancy.
➡️ For sudden bone fractures or severe trauma, urgent medical attention is necessary.
➡️ Early consultation ensures accurate diagnosis and prevents complications such as fractures, deformity, or chronic pain.
Care and Treatment
Management focuses on treating the underlying cause and relieving pain:
Highlights:
➡️ Pain Management: NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or prescription analgesics.
➡️ Addressing Underlying Causes:
- Fracture care: immobilization, casting, or surgical fixation
- Osteoporosis: calcium, vitamin D supplementation, and bisphosphonates
- Infection: antibiotics or antiviral therapy as indicated
- Cancer-related pain: chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery
➡️ Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Improve mobility, strength, and bone health.
➡️ Lifestyle Modifications: Adequate nutrition, weight-bearing exercises, and fall prevention.
➡️ Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular imaging and lab tests to track bone health.
➡️ Patient Education: Guidance on symptom recognition, fracture prevention, and bone-strengthening strategies.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive bone care and musculoskeletal health services:
Highlights:
➡️ Orthopedic Clinics and Hospitals: Diagnosis, fracture management, and surgical interventions.
➡️ Bone Density and Metabolic Testing: Screening for osteoporosis and metabolic bone disorders.
➡️ Pain Management Centers: Advanced analgesic therapy and minimally invasive interventions.
➡️ Rehabilitation Services: Physiotherapy and occupational therapy for bone and joint recovery.
➡️ Oncology Services: Diagnosis and treatment of bone tumors or metastases.
➡️ Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration between orthopedists, endocrinologists, oncologists, and physiotherapists.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Structured evaluation, imaging, and follow-up care for international patients.