Overview
Abdominal pain is a common symptom that affects individuals of all ages and can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. It may arise from problems in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary system, reproductive organs, or other systemic conditions. While occasional abdominal pain is often harmless, persistent or severe pain may indicate an underlying medical issue requiring evaluation. In Korea, hospitals and specialized clinics provide advanced diagnostic testing, medical treatment, and holistic care to identify the cause and relieve pain effectively.
Key Facts
▶ Prevalence: Abdominal pain is one of the most frequent complaints in clinics worldwide.
▶ Types: Acute (sudden onset) or chronic (lasting weeks or months).
▶ Common Locations: Upper abdomen, lower abdomen, around the belly button, or generalized discomfort.
▶ Causes: Gastrointestinal infections, inflammation, food intolerances, urinary issues, stress, or structural abnormalities.
▶ Treatment Options in Korea: Diagnostic imaging, medications, dietary management, minimally invasive procedures, and integrative therapies.
What is Abdominal Pain?
Abdominal pain refers to discomfort or pain in the area between the chest and pelvis. It can be mild, intermittent, or severe, depending on the cause. Pain may be localized to a specific region or generalized across the abdomen.
▶ Acute Abdominal Pain: Sudden onset pain, often caused by infections, injuries, or food-related issues.
▶ Chronic Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain lasting weeks or months, sometimes linked to functional gastrointestinal disorders, stress, or systemic illness.
▶ Localized vs. Diffuse Pain: Location can help identify specific organ involvement (e.g., appendicitis, gallbladder issues).
Note: Abdominal pain is a symptom rather than a diagnosis and requires careful evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
What Symptoms Are Related to Abdominal Pain?
▶ Cramping or Sharp Pain: Often associated with digestive disturbances.
▶ Nausea and Vomiting: Common in infections, food poisoning, or gastrointestinal disorders.
▶ Diarrhea or Constipation: May accompany digestive issues or inflammatory conditions.
▶ Bloating and Gas: Can result from dietary factors or digestive imbalances.
▶ Fever or Chills: Suggests infection or systemic inflammation.
▶ Loss of Appetite: Pain may reduce desire to eat.
▶ Fatigue or Irritability: Persistent pain can affect mood and energy levels.
▶ Pain Migration: Pain that shifts location, such as from the belly button to the lower right abdomen, may indicate appendicitis.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Abdominal pain can originate from gastrointestinal, urinary, reproductive, or systemic causes:
▶ Gastrointestinal Infections: Viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections causing stomach upset.
▶ Constipation: Hard stools causing bloating, cramping, and discomfort.
▶ Food Intolerances or Allergies: Lactose intolerance, gluten sensitivity, or other dietary triggers.
▶ Functional Disorders: Stress or psychological factors affecting gut function.
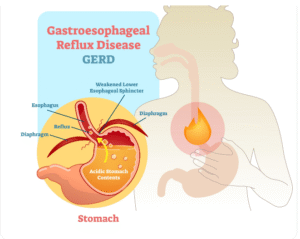
▶ Inflammatory Conditions: Appendicitis, gastritis, peptic ulcers, or inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis).
▶ Urinary Tract Disorders: UTIs, kidney stones, or bladder inflammation.
▶ Gynecological Issues (in females): Menstrual cramps, ovarian cysts, or endometriosis.
▶ Medications or Toxins: Certain drugs or ingestion of harmful substances.
▶ Structural Problems: Hernias, tumors, or congenital anomalies.
When Should I See a Doctor?
▶ Severe or Sudden Pain: Especially if localized or accompanied by other alarming symptoms.
▶ Persistent Pain: Lasting more than a few days or interfering with daily activities.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Fever, vomiting, diarrhea, blood in stool or vomit.
▶ Weight Loss or Appetite Loss: Unexplained changes may indicate chronic conditions.
▶ Urinary or Gynecological Symptoms: Pain during urination, unusual discharge, or menstrual irregularities.
▶ Behavioral Changes: Irritability, lethargy, or inability to perform daily tasks.
Tip: Early evaluation ensures proper diagnosis, timely treatment, and prevention of potential complications.
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause, severity, and duration of abdominal pain:
▶ Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding trigger foods and maintaining a balanced diet.
▶ Hydration: Drinking adequate fluids, especially with vomiting or diarrhea.
▶ Medications: Pain relievers, antispasmodics, antibiotics, or acid-reducing medications as prescribed.
▶ Lifestyle Changes: Stress management, regular exercise, and healthy sleep patterns.
▶ Rest and Comfort Measures: Heat therapy, gentle abdominal massage, or relaxation techniques.
▶ Probiotics: Supporting gut microbiome health in certain digestive disorders.
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Evaluation:
▶ Pediatric or Adult Gastroenterology Consultation: Comprehensive assessment for acute or chronic pain.
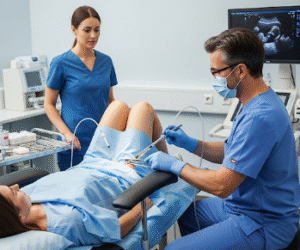
▶ Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to identify structural or inflammatory causes.
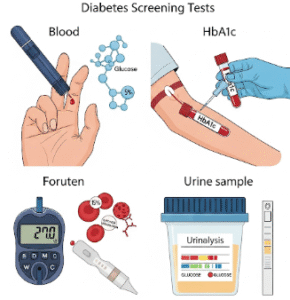
▶ Laboratory Tests: Blood, stool, or urine tests to detect infection or metabolic disorders.
Advanced Treatments:
▶ Endoscopic Procedures: For evaluation or treatment of ulcers, polyps, or other gastrointestinal abnormalities.
▶ Surgical Intervention: Required for appendicitis, hernia repair, or severe structural issues.
▶ Medication Management: Tailored therapies for digestive, urinary, or inflammatory conditions.
Rehabilitation & Support:
▶ Nutritional Counseling: Personalized dietary plans to prevent recurrence.
▶ Behavioral Therapy: For functional abdominal pain or stress-related gastrointestinal issues.
▶ Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring to track symptom improvement and prevent complications.
Outcome: With prompt assessment and comprehensive treatment in Korea, most cases of abdominal pain are effectively managed, allowing patients to resume normal activities and maintain optimal digestive and overall health.