Overview
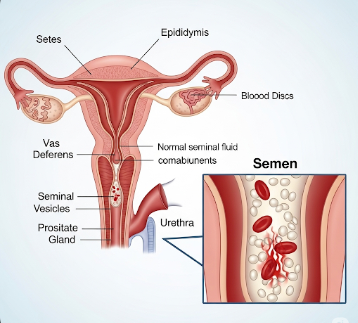
Blood in semen, medically known as hematospermia, is the presence of red or brown discoloration in ejaculate. While often alarming, it is usually benign and self-limiting, particularly in men under 40. However, persistent or recurrent hematospermia may indicate underlying urological conditions such as infections, inflammation, or, rarely, tumors. In Korea, urology specialists and hospitals provide advanced diagnostic tools, including imaging and laboratory tests, along with targeted treatments to identify and address the cause of blood in semen effectively.
Key Facts
▶ Prevalence: Relatively uncommon but can occur at any age; most cases are benign.
▶ Appearance: Blood may range from pink, red, to brown in the ejaculate.
▶ Duration: Often transient, lasting for a single ejaculation or a few occurrences.
▶ Causes: Infections, inflammation, trauma, high blood pressure, or prostate issues.
▶ Treatment Options in Korea: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, minimally invasive procedures, and regular monitoring.
What is Blood in Semen?
Blood in semen, or hematospermia, is the visible presence of blood within ejaculate. It can be painless or accompanied by other symptoms such as discomfort during urination or ejaculation.
▶ Acute Hematospermia: Sudden appearance, usually linked to infection or trauma.
▶ Chronic or Recurrent Hematospermia: Persistent presence, potentially indicating an underlying medical issue.
▶ Benign vs. Pathological: Most cases in younger men are benign, whereas older men or those with additional urological symptoms require thorough evaluation.
Note: While anxiety-inducing, most cases of blood in semen are temporary and respond well to medical management.
What Symptoms Are Related to Blood in Semen?
▶ Visible Blood in Ejaculate: Pink, red, or brown discoloration.
▶ Pain or Discomfort: Mild pain or burning sensation during ejaculation or urination.
▶ Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Increased frequency, urgency, or difficulty urinating.
▶ Swelling or Tenderness: In the prostate, testes, or epididymis in cases of infection or inflammation.
▶ Fever or Malaise: May occur with infections.
▶ No Symptoms: Often, hematospermia occurs without pain or other noticeable changes.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Blood in semen can result from various urological, systemic, or traumatic factors:
▶ Prostate Issues: Inflammation (prostatitis), enlargement, or rarely, prostate tumors.
▶ Infections: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), urinary tract infections (UTIs), or epididymitis.
▶ Vascular Causes: Trauma, vigorous sexual activity, or recent medical procedures like biopsy.
▶ Seminal Vesicle Disorders: Inflammation or cysts affecting the seminal vesicles.
▶ High Blood Pressure: Can occasionally lead to minor bleeding.
▶ Medications: Blood thinners or anticoagulants may increase risk of hematospermia.
▶ Systemic Conditions: Liver disease or bleeding disorders in rare cases.
Note: Age, medical history, and recurrence help determine whether the cause is benign or requires intervention.
When Should I See a Doctor?
▶ Persistent or Recurrent Blood: Multiple occurrences or ongoing episodes.
▶ Pain or Discomfort: Accompanied by fever, swelling, or urinary symptoms.
▶ Older Age: Men over 40 should seek evaluation to rule out serious causes.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Blood in urine, painful ejaculation, or pelvic pain.
▶ Underlying Health Issues: Men on blood thinners or with liver or clotting disorders.
Tip: While most hematospermia is benign, early evaluation ensures correct diagnosis and peace of mind.
Care and Treatment
Management depends on the underlying cause and severity:
▶ Observation: Single, mild episodes may resolve spontaneously without intervention.
▶ Antibiotics: For infections affecting the prostate, urethra, or seminal vesicles.
▶ Anti-inflammatory Medications: To reduce pain or inflammation in urogenital tissues.
▶ Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding vigorous sexual activity until resolution.
▶ Follow-Up Testing: Imaging or lab tests if symptoms persist or worsen.
▶ Addressing Medical Conditions: Blood pressure control or adjustment of medications if contributing.
Additional Measures: Keeping track of symptoms, ejaculate color, and frequency helps clinicians make accurate assessments.
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Evaluation:
▶ Urology Consultation: Comprehensive physical exam and detailed medical history.
▶ Laboratory Tests: Urine analysis, semen culture, and STI screening.
▶ Imaging: Ultrasound or MRI to evaluate the prostate, seminal vesicles, and other structures.
Advanced Interventions:
▶ Minimally Invasive Procedures: Endoscopic evaluation or treatment for cysts or obstructions.
▶ Targeted Therapy: Antibiotics or anti-inflammatory treatment guided by test results.
▶ Monitoring: Regular follow-up to ensure resolution and prevent recurrence.
Rehabilitation & Support:
▶ Patient Education: Information on sexual activity, hygiene, and symptom tracking.
▶ Psychological Support: Counseling for anxiety caused by visible blood in semen.
▶ Specialist Clinics: Korean urology centers provide integrated care for both diagnosis and long-term follow-up.
Outcome: With proper evaluation and targeted treatment in Korea, most cases of blood in semen resolve completely, allowing individuals to maintain sexual health and confidence. Chronic or complex cases benefit from ongoing monitoring and specialist care.