Overview
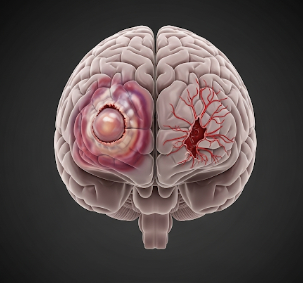
Brain injury refers to any damage to the brain that affects its normal function. It can result from trauma, lack of oxygen, infections, strokes, or other medical conditions. Brain injuries range from mild concussions to severe, life-threatening injuries, and can lead to temporary or permanent neurological deficits.
In Korea, brain injuries are treated in neurology, neurosurgery, and rehabilitation centers using advanced diagnostic imaging, surgical interventions, and comprehensive rehabilitation programs. The goal is to stabilize patients, restore neurological function, and optimize quality of life. Korean hospitals provide multidisciplinary care, including neurosurgeons, neurologists, physiotherapists, and neuropsychologists.
What is Brain Injury?
Brain injury can be broadly classified as:
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Caused by external forces such as falls, car accidents, sports injuries, or assaults
- Mild TBI: Concussions with temporary symptoms
- Moderate to severe TBI: Prolonged loss of consciousness or significant neurological deficits
- Acquired Brain Injury (ABI): Occurs after birth due to stroke, infections, lack of oxygen (anoxia or hypoxia), tumors, or toxic exposure
Brain injuries can be focal, affecting a specific brain region, or diffuse, impacting multiple areas. The location and severity of the injury determine the type and extent of neurological dysfunction.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on severity, location, and cause of the injury:
- Mild brain injury:
- Headache
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion or disorientation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Memory or concentration difficulties
- Moderate to severe brain injury:
- Loss of consciousness or coma
- Persistent or worsening headache
- Seizures
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
- Speech and language difficulties
- Vision or hearing problems
- Emotional and behavioral changes, including irritability, anxiety, or depression
Causes
Brain injury can result from physical, medical, or environmental factors:
- Traumatic causes: Falls, road traffic accidents, sports injuries, workplace accidents, and assaults
- Medical causes: Stroke, brain hemorrhage, infections such as meningitis or encephalitis, brain tumors
- Hypoxic or anoxic injury: Lack of oxygen due to drowning, cardiac arrest, or suffocation
- Toxic exposure: Poisoning, drugs, or alcohol leading to brain cell damage
- Degenerative conditions: Rarely, progressive diseases may cause cumulative brain injury
Risk Factors
- Age extremes: Young children and older adults are more susceptible
- Male gender: Higher incidence of traumatic brain injury due to occupational and lifestyle risks
- High-risk activities: Sports, motorcycling, or driving without protective measures
- Pre-existing medical conditions: Stroke, seizures, or clotting disorders
- Substance abuse: Alcohol and recreational drugs increase risk of accidents
- Previous brain injury: History of prior TBI increases susceptibility
Complications
Brain injury can lead to short-term and long-term complications:
- Cognitive impairment: Memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and impaired judgment
- Physical disabilities: Weakness, paralysis, and coordination problems
- Sensory deficits: Vision, hearing, or speech difficulties
- Emotional and behavioral changes: Mood swings, depression, anxiety, or aggression
- Seizures and epilepsy
- Hydrocephalus: Fluid accumulation in the brain
- Coma or persistent vegetative state in severe cases
- Death in extreme cases if untreated
Prevention
While some brain injuries are unavoidable, preventive measures can significantly reduce risk:
- Wearing helmets and protective gear during sports, cycling, or motorcycling
- Using seat belts and child safety seats in vehicles
- Fall prevention measures at home, especially for older adults
- Avoiding high-risk behaviors such as reckless driving or alcohol use
- Early treatment of medical conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease
- Safe workplace practices and protective equipment
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining severity and treatment:
- CT scan: Rapid identification of bleeding, fractures, or swelling
- MRI: Detailed imaging for soft tissue injuries and diffuse axonal injury
- Neurological examination: Assesses consciousness, motor function, and reflexes
- Electroencephalography (EEG): Detects seizure activity
- Blood tests: Evaluate metabolic or toxic causes of brain injury
Medical Management
- Acute care: Stabilization of airway, breathing, and circulation
- Medications:
- Anti-seizure drugs
- Pain management
- Diuretics or osmotic agents to reduce brain swelling
- Sedatives for agitation
- Monitoring in ICU: Continuous neurological and vital sign observation
Surgical Management
Surgery may be required in moderate to severe cases:
- Craniotomy: Removal of hematomas or fractured bone fragments
- Decompressive craniectomy: Relieves intracranial pressure
- Ventriculostomy: Drains excess cerebrospinal fluid in hydrocephalus
- Repair of skull fractures or vascular injuries
Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy: Restores mobility, balance, and coordination
- Occupational therapy: Helps regain daily living skills
- Speech and language therapy: For communication difficulties
- Cognitive therapy: Improves memory, attention, and problem-solving skills
- Psychological support: Counseling for depression, anxiety, or behavioral changes
- Family education: Guidance on care and recovery strategies
Prognosis
The prognosis of brain injury depends on severity, cause, and timing of treatment:
- Mild injuries: Usually recover fully within days to weeks
- Moderate injuries: Recovery may take months with residual cognitive or physical deficits
- Severe injuries: Risk of permanent disability or death; rehabilitation can improve independence and quality of life
- Early intervention in Korean hospitals, combining acute care, surgery, and rehabilitation, significantly enhances outcomes
- Long-term follow-up ensures monitoring of neurological function and prevention of secondary complications
With state-of-the-art emergency care, neurosurgical expertise, and comprehensive rehabilitation programs, Korea offers world-class treatment for brain injury, aiming to minimize damage, restore function, and improve patient quality of life.