Overview
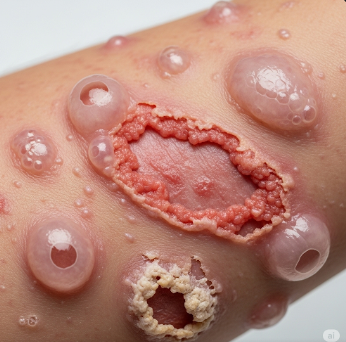
Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder that primarily affects older adults, causing tense, fluid-filled blisters (bullae) on the skin. Unlike other blistering diseases, BP typically does not involve the mucous membranes extensively.
In Korea, Bullous Pemphigoid is managed in dermatology clinics and specialized hospitals, where advanced diagnostic techniques and targeted therapies are available. Korean dermatologists focus on early diagnosis, symptom control, and minimizing complications, ensuring effective long-term management for patients.
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous Pemphigoid is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks components of the skin, specifically the basement membrane that separates the epidermis from the dermis. This attack leads to:
- Formation of large, tense blisters filled with fluid
- Reddened or inflamed skin surrounding blisters
- Itching and discomfort, often severe before blisters appear
The condition is chronic, with periods of flare-ups and remission, and while it is rarely life-threatening, it can significantly affect quality of life if untreated.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid often develop gradually and may include:
- Large, tense blisters on the skin, especially on the arms, legs, abdomen, and groin
- Red, itchy, or inflamed patches preceding blister formation
- Fluid leakage from ruptured blisters
- Pain, tenderness, or burning sensation in affected areas
- Erosions and crusts when blisters rupture
- Secondary infections in severe or untreated cases
- Chronic itching (pruritus), sometimes severe and disruptive to sleep
Symptoms can vary in intensity, and older adults are more likely to experience widespread blistering and discomfort.
Causes
Bullous Pemphigoid is caused by an autoimmune response in which the body produces antibodies against proteins in the skin’s basement membrane (BP180 and BP230). Contributing factors include:
- Age-related changes in the immune system, increasing susceptibility in older adults
- Genetic predisposition, although rare
- Medications such as diuretics, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drugs in some cases
- Underlying neurological conditions, including Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or dementia
- Environmental triggers, including physical trauma or infections, which may precipitate flare-ups
Risk Factors
- Older age, particularly individuals over 60 years
- Neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease
- Certain medications, including loop diuretics, penicillin, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- History of autoimmune conditions
- Skin trauma or chronic sun exposure in some cases
Complications
If left untreated, Bullous Pemphigoid can lead to several complications:
- Secondary bacterial infections, particularly in ruptured blisters
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalance due to widespread blistering
- Sepsis, in severe cases with infected lesions
- Pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility from extensive blistering
- Emotional and psychological impact, including anxiety or depression related to chronic skin disease
- Side effects from long-term corticosteroid therapy, such as osteoporosis, diabetes, or hypertension
Prevention
While autoimmune diseases cannot be fully prevented, certain measures can reduce flare-ups and complications:
- Prompt treatment of early symptoms, including redness or itching
- Avoiding skin trauma and protecting the skin from harsh chemicals or friction
- Monitoring medications that may trigger or worsen BP
- Maintaining overall skin hygiene to prevent secondary infections
- Regular follow-up with dermatologists to monitor disease activity and adjust treatment
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on clinical evaluation, skin biopsy, and laboratory tests:
- Physical examination to observe blisters, redness, and skin erosions
- Skin biopsy with direct immunofluorescence to detect antibodies at the basement membrane
- Blood tests to identify circulating autoantibodies (BP180 and BP230)
- Differential diagnosis to rule out other blistering disorders such as pemphigus vulgaris or dermatitis herpetiformis
Medical Management
Treatment aims to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent complications:
- Topical corticosteroids, especially for localized disease
- Oral corticosteroids for more severe or widespread cases
- Immunosuppressive agents, including azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, or methotrexate, to reduce immune response
- Antibiotics if secondary infection develops
- Adjunct therapies, such as antihistamines, to relieve itching and discomfort
Advanced Therapies
- Biologic treatments (e.g., rituximab) in refractory cases
- Plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in severe, resistant disease
- Hospitalization for extensive or complicated cases, especially when infections or electrolyte imbalances occur
Supportive Care
- Gentle wound care to prevent infection
- Moisturizers and emollients to protect skin
- Pain management for blister-related discomfort
- Regular monitoring of treatment response and side effects of medications
Prognosis
With appropriate treatment, the prognosis of Bullous Pemphigoid is generally favorable, though the condition may require long-term management:
- Localized disease often responds well to topical corticosteroids
- Severe or widespread disease requires systemic therapy but can be effectively controlled
- Early diagnosis and treatment reduce the risk of complications such as infections and long-term skin damage
- Korean dermatology centers provide advanced diagnostics, immunosuppressive therapies, and supportive care, ensuring improved quality of life for patients
- Relapses are possible, so ongoing follow-up and lifestyle measures are important
With multidisciplinary care, advanced medical therapies, and vigilant monitoring, Bullous Pemphigoid in Korea can be managed effectively, allowing patients to reduce symptoms, prevent complications, and maintain healthy skin.