Overview
Back injuries encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the muscles, ligaments, bones, nerves, and discs in the back. These injuries can result from sudden trauma, repetitive strain, sports accidents, workplace hazards, or degenerative changes in the spine over time. Back injuries may cause mild, temporary discomfort or severe, long-lasting pain that significantly affects mobility and daily activities. In Korea, back injuries are commonly seen in both younger adults—often due to sports or exercise-related accidents—and older adults experiencing age-related spinal degeneration. Thanks to its advanced medical infrastructure, Korea offers comprehensive diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation services for all types of back injuries, combining modern medicine with traditional Korean therapies to support faster recovery and long-term spine health.
What are Back Injuries?
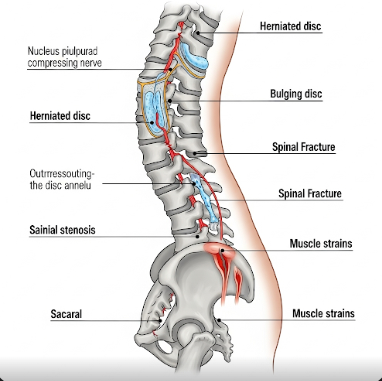
Back injuries refer to any damage or trauma to the structures of the back, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, vertebrae, intervertebral discs, and nerves. They can occur suddenly, such as from a fall or collision, or gradually due to repetitive movements and poor posture. Back injuries are often classified into:
- Acute injuries – occurring suddenly, often due to accidents, sports impacts, or heavy lifting
- Chronic injuries – developing over time from repeated strain, poor ergonomics, or degenerative spine conditions
- Traumatic injuries – involving fractures, dislocations, or severe soft tissue damage
- Overuse injuries – caused by repetitive motion, often in certain professions or sports
Common examples of back injuries include muscle strains, ligament sprains, herniated discs, vertebral fractures, and spinal cord injuries.
Symptoms
The symptoms of back injuries vary depending on the specific structure affected and the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp, stabbing, or aching pain in the back
- Muscle spasms or tightness
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Swelling or bruising in the injured area
- Pain radiating to the buttocks, legs, or arms (nerve involvement)
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the extremities
- Weakness in the legs or difficulty walking
- In severe cases, loss of bladder or bowel control (medical emergency)
Causes
Back injuries can be caused by various factors, such as:
- Trauma and accidents – car collisions, falls, sports injuries, or workplace accidents
- Improper lifting techniques – lifting heavy objects without bending the knees or keeping the back straight
- Overexertion – pushing the back beyond its capacity during exercise or physical labor
- Repetitive strain – repeated twisting, bending, or pulling movements
- Sports-related activities – high-impact sports like gymnastics, football, or weightlifting
- Poor posture – sitting, standing, or sleeping in awkward positions over long periods
- Degenerative conditions – such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and degenerative disc disease
- Occupational hazards – jobs involving heavy lifting, vibrations, or prolonged standing/sitting
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of back injuries:
- Age, especially over 40 when degenerative changes become more common
- Lack of physical conditioning and weak core muscles
- Excess body weight, which puts added stress on the spine
- Occupations involving repetitive lifting, twisting, or vibration exposure
- Participation in high-impact or contact sports
- Pre-existing spine conditions like scoliosis or spinal stenosis
- Poor ergonomic setup at workstations or in vehicles
- Smoking, which weakens spinal discs and slows healing
Complications
If left untreated or improperly managed, back injuries can lead to:
- Chronic back pain that limits daily activities
- Persistent nerve damage causing weakness or numbness
- Reduced mobility and flexibility
- Muscle imbalances and posture problems
- Long-term dependency on pain medications
- Psychological effects such as depression or anxiety due to prolonged pain
- Permanent disability in severe cases, especially with spinal cord involvement
Prevention
Preventing back injuries involves a combination of good physical habits, proper ergonomics, and awareness during activities:
- Maintain strong core muscles through regular exercise
- Practice correct lifting techniques—bend at the knees, keep the back straight, and hold loads close to the body
- Use ergonomically designed chairs, desks, and tools
- Avoid prolonged sitting—stand, stretch, and walk periodically
- Wear appropriate protective gear during sports or heavy labor
- Maintain a healthy body weight to reduce spinal strain
- Stay flexible with stretching exercises to reduce muscle tension
- Ensure workspaces are arranged to minimize awkward postures
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers a full spectrum of treatments for back injuries, ranging from conservative care to advanced surgical interventions.
1. Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the first step in managing back injuries effectively. Korean hospitals use:
- X-rays to detect fractures, bone alignment issues, and arthritis
- MRI scans for detailed images of soft tissues, discs, and nerves
- CT scans for complex bone injuries or fractures
- Ultrasound for muscle or ligament injuries
- Electromyography (EMG) to assess nerve function and damage
2. Medical Treatments
For mild to moderate back injuries, conservative treatments may include:
- Pain relief medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Muscle relaxants to reduce spasms
- Physical therapy to restore flexibility, strength, and posture
- Heat or cold therapy to reduce swelling and ease discomfort
- Epidural steroid injections for nerve inflammation
3. Surgical Options
In severe cases where conservative methods are ineffective, surgical interventions may be necessary:
- Discectomy to remove herniated disc material pressing on nerves
- Spinal fusion to stabilize damaged vertebrae
- Laminectomy to relieve spinal canal pressure
- Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for fractures due to osteoporosis
- Minimally invasive spine surgery for quicker recovery and less postoperative pain
4. Traditional Korean Medicine
Korea also integrates centuries-old therapeutic methods into modern back injury care:
- Acupuncture to stimulate healing and relieve pain
- Chuna manual therapy to improve spinal alignment and mobility
- Herbal medicine to reduce inflammation and support recovery
- Cupping therapy to relieve muscle tension and improve blood flow
5. Rehabilitation and Support
Post-treatment care focuses on preventing recurrence and ensuring long-term spinal health:
- Customized exercise programs tailored to the patient’s injury
- Posture and movement training for daily activities
- Nutritional guidance for bone and muscle health
- Regular follow-ups to monitor progress and detect any complications early
6. Medical Tourism for Back Injuries in Korea
Many international patients choose Korea for back injury treatment due to:
- World-class spine specialists with high surgical success rates
- Access to advanced diagnostic imaging and minimally invasive surgery
- Rehabilitation programs that combine Western physiotherapy with Korean traditional medicine
- Competitive treatment costs compared to the US, Japan, or Europe