Overview
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection caused by an imbalance in the natural bacteria found in the vagina. Normally, the vagina contains a healthy balance of bacteria, with lactobacilli being the dominant type that helps maintain a slightly acidic environment. When the number of lactobacilli decreases and harmful bacteria grow excessively, bacterial vaginosis develops. While BV is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection (STI), sexual activity can influence its occurrence. In Korea, women have access to high-quality gynecological care, accurate diagnostic tests, and effective treatments that restore vaginal health. Korean hospitals and clinics also emphasize education on prevention and recurrence management.
What is Bacterial Vaginosis?
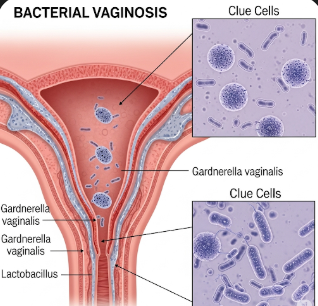
Bacterial vaginosis is an imbalance of the vaginal microbiome that leads to an overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, and other species. These bacteria replace the normal lactobacilli, disrupting the vaginal pH and leading to symptoms like unusual discharge and odor. While BV can occur in women of all ages, it is most common among women of reproductive age. It can also increase the risk of developing other infections, including STIs, and can complicate pregnancy outcomes if left untreated.
Symptoms
Some women with bacterial vaginosis have no noticeable symptoms, while others may experience:
- Thin, watery vaginal discharge, often gray or white in color
- Strong, fish-like vaginal odor, especially after sexual intercourse
- Mild vaginal itching or irritation
- Burning sensation during urination
It is important to note that BV symptoms can resemble those of yeast infections or STIs, so accurate diagnosis by a healthcare provider is essential.
Causes
Bacterial vaginosis is caused by a change in the natural vaginal flora. Factors that may trigger this imbalance include:
- Having a new sexual partner or multiple partners
- Douching, which disrupts the natural pH and bacterial balance
- Lack of condom use during intercourse
- Smoking, which can affect immune response and vaginal health
- Hormonal changes, including those caused by birth control or pregnancy
- Use of antibiotics that alter bacterial levels in the body
Risk Factors
Certain factors make women more likely to develop BV:
- Being sexually active with multiple partners
- Previous episodes of bacterial vaginosis
- Vaginal douching habits
- Use of intrauterine devices (IUDs) for birth control
- Low levels of lactobacilli in the vaginal microbiome
- Weakened immune system due to illness or medications
Complications
While bacterial vaginosis is not typically dangerous, it can cause complications if left untreated:
- Increased risk of acquiring sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, and HIV
- Higher risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause infertility
- Pregnancy-related complications, including premature birth and low birth weight
- Post-surgical infections after gynecological procedures such as hysterectomy or abortion
Prevention
To reduce the risk of bacterial vaginosis and its recurrence, the following preventive measures are recommended:
- Avoid vaginal douching, as it disrupts the natural bacterial balance
- Use condoms during sexual activity to reduce bacterial exchange
- Maintain good genital hygiene without using harsh soaps or scented products
- Limit the number of sexual partners
- Wear breathable cotton underwear to maintain a dry, balanced vaginal environment
- Seek medical advice promptly if symptoms return after treatment
Treatment Options in Korea
1. Diagnosis
Korean gynecologists use accurate and efficient diagnostic methods to confirm BV:
- Pelvic examination – to check for discharge and odor
- pH testing – BV usually causes a vaginal pH higher than 4.5
- Microscopic examination (wet mount) – to identify “clue cells,” which are vaginal cells coated with bacteria
- Whiff test – adding potassium hydroxide to a sample to check for the characteristic fish-like odor
2. Medical Treatments
Bacterial vaginosis is treated with antibiotics to restore the balance of vaginal bacteria. Common options include:
- Metronidazole (oral or vaginal gel) – taken for 5–7 days
- Clindamycin cream or capsules – an alternative for women who cannot tolerate metronidazole
- Tinidazole – another oral antibiotic option for recurrent BV cases
Korean clinics follow evidence-based guidelines to ensure optimal dosage and prevent antibiotic resistance.
3. Probiotics and Vaginal Health Support
Many Korean gynecologists recommend probiotics alongside antibiotic treatment to restore lactobacillus populations. These probiotics may be taken orally or applied vaginally, helping maintain a healthy pH and prevent recurrence.
4. Lifestyle and Recurrence Management
In Korea, women’s health clinics offer counseling and education on lifestyle changes to reduce the recurrence of BV, such as avoiding irritants, practicing safe sex, and monitoring for early symptoms. For women with frequent relapses, doctors may suggest longer-term treatment with vaginal probiotics or low-dose antibiotics.
5. Pregnancy Considerations
For pregnant women, treatment of BV is essential to lower the risk of complications. Korean obstetricians are skilled in providing safe medication regimens that do not harm the developing baby while effectively clearing the infection.
6. Medical Tourism for Gynecological Care
South Korea’s advanced gynecology services attract international patients seeking confidential, high-quality care for conditions like BV. Benefits include:
- Discreet, patient-centered services in modern clinics
- Bilingual staff for international patients
- Comprehensive sexual health checkups alongside BV treatment
- Integration of traditional Korean herbal approaches for holistic recovery when requested