Overview
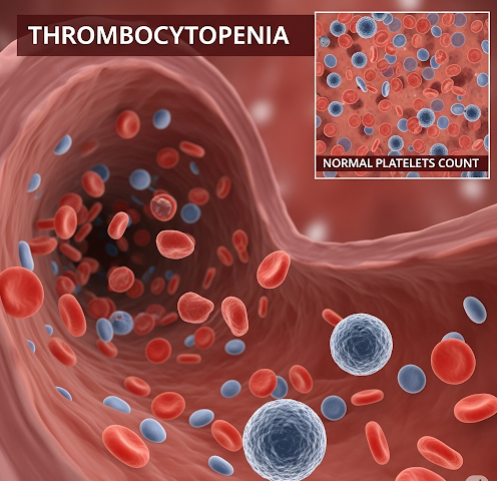
Thrombocytopenia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally low number of platelets (thrombocytes) in the blood. Platelets are critical for blood clotting, and a reduced platelet count increases the risk of excessive bleeding, bruising, and in severe cases, life-threatening hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia can be a primary disorder or secondary to other medical conditions, medications, or infections. South Korea offers advanced diagnostic facilities, hematology specialists, and treatment options, including medication, platelet transfusions, and specialized therapies, making early detection and management highly effective.
What is Thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia occurs when the platelet count falls below the normal range of 150,000–450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. It can be classified based on cause, severity, and duration:
- Mild thrombocytopenia: Slightly below normal platelet levels, often asymptomatic
- Moderate thrombocytopenia: May cause easy bruising, nosebleeds, or prolonged bleeding
- Severe thrombocytopenia: Significantly increases the risk of spontaneous bleeding, including internal hemorrhage
- Acute vs. chronic: Acute cases develop quickly, often due to infection or drug reactions, whereas chronic cases persist for months or years
In South Korea, hematology centers use comprehensive laboratory testing and clinical evaluation to diagnose the specific type and severity of thrombocytopenia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia vary depending on platelet count and underlying cause. Common manifestations include:
- Easy or excessive bruising (ecchymosis)
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts or minor injuries
- Frequent nosebleeds or gum bleeding
- Small red or purple spots on the skin (petechiae)
- Fatigue due to blood loss in severe cases
- Blood in urine or stool
- In extreme cases, internal bleeding or hemorrhagic complications
Some individuals with mild thrombocytopenia may not experience noticeable symptoms, making routine blood tests important for early detection.
Causes
Thrombocytopenia can result from decreased platelet production, increased destruction, or abnormal sequestration. Common causes include:
- Bone marrow disorders: Leukemia, aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndromes
- Autoimmune diseases: Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) where antibodies destroy platelets
- Medications: Chemotherapy, certain antibiotics, or heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- Infections: Viral infections such as hepatitis, HIV, or dengue fever
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of vitamin B12 or folate affecting platelet production
- Liver disease or splenomegaly: Enlarged spleen sequesters platelets, reducing circulating levels
South Korean hospitals utilize laboratory analysis, bone marrow studies, and imaging to identify underlying causes and guide treatment.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing thrombocytopenia:
- Autoimmune disorders such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
- Viral or bacterial infections affecting platelet production
- Use of medications known to lower platelet counts
- Chronic liver disease or splenic enlargement
- Genetic disorders affecting blood cell production
- Advanced age, which may influence platelet function and production
Preventive strategies in South Korea include careful monitoring of at-risk patients, medication review, and early screening in individuals with chronic illnesses.
Complications
If untreated or severe, thrombocytopenia can lead to serious complications:
- Excessive bleeding, even from minor injuries
- Gastrointestinal bleeding or blood in urine
- Intracranial hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening
- Anemia due to chronic blood loss
- Complications during surgery or invasive procedures
- Increased susceptibility to bruising and trauma-related injuries
Timely intervention in South Korea with specialized hematology care reduces these risks and improves patient outcomes.
Prevention
While not all cases of thrombocytopenia can be prevented, certain measures help reduce risk:
- Avoiding medications that can lower platelet counts unless prescribed
- Prompt treatment of infections that may affect platelet levels
- Maintaining a balanced diet with adequate vitamin B12, folate, and iron
- Monitoring platelet counts in high-risk populations, such as patients with autoimmune diseases or on chemotherapy
- Practicing safety measures to prevent trauma or injury that could trigger bleeding
South Korean healthcare emphasizes patient education and early detection to prevent complications from thrombocytopenia.
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for thrombocytopenia depends on the underlying cause, severity, and risk of bleeding:
Diagnosis:
- Complete blood count (CBC) to measure platelet levels
- Peripheral blood smear to examine platelet morphology
- Bone marrow biopsy for evaluation of production disorders
- Imaging studies to detect splenomegaly or organ involvement
- Autoantibody testing for immune-mediated causes
Medical Treatments:
- Medications: Corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune thrombocytopenia
- Platelet transfusions: Used in severe cases or before surgery to prevent bleeding
- Medications to stimulate platelet production: Thrombopoietin receptor agonists
- Treatment of underlying causes: Addressing infections, liver disease, or discontinuing causative medications
Supportive Care:
- Avoiding activities that increase bleeding risk
- Using soft-bristled toothbrushes and avoiding sharp instruments
- Education on recognizing signs of severe bleeding
Surgical or Advanced Interventions:
- Splenectomy: Surgical removal of the spleen in cases of chronic immune thrombocytopenia unresponsive to medication
- Stem cell therapy: In rare cases of bone marrow failure
South Korean hospitals provide multidisciplinary care involving hematologists, internists, and specialized nursing teams to ensure safe, effective management of thrombocytopenia.