Overview
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, usually caused by viral or bacterial infections. It commonly affects children and young adults but can occur at any age. Symptoms include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. If untreated, bacterial tonsillitis, especially from Streptococcus pyogenes, can lead to complications such as rheumatic fever or peritonsillar abscess. South Korea provides advanced diagnostic and treatment options, including rapid bacterial testing, antibiotic therapy, minimally invasive tonsillectomy procedures, and supportive care, ensuring effective recovery and prevention of recurrent infections.
What is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis occurs when the palatine tonsils—lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat—become inflamed due to infection. It can be acute, lasting a few days to weeks, or chronic/recurrent, with repeated episodes over months or years. Tonsillitis is typically categorized based on the cause:
- Viral tonsillitis: Caused by viruses such as adenovirus, influenza, or Epstein-Barr virus. It is the most common form.
- Bacterial tonsillitis: Usually caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A streptococcus). Bacterial infections require antibiotic treatment.
Symptoms vary with severity and causative agent. In some cases, inflammation can extend to surrounding structures, including the pharynx and adenoids, leading to pharyngotonsillitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of tonsillitis range from mild discomfort to severe pain affecting swallowing and daily activities:
- Sore throat: Often sudden in onset and worsens with swallowing
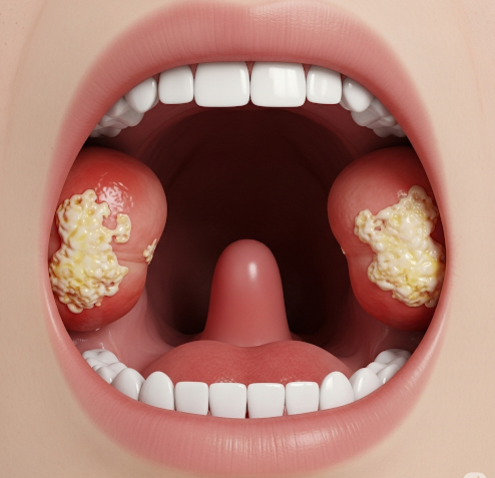
- Red, swollen tonsils: Sometimes with white or yellow exudate
- Fever: Mild to high-grade, more common in bacterial infections
- Painful swallowing (odynophagia): Can affect eating and drinking
- Swollen lymph nodes: Particularly in the neck and jaw area
- Bad breath (halitosis): Due to bacterial overgrowth
- Voice changes: Muffled or hoarse voice in severe cases
- Ear pain: Referred pain due to shared nerve pathways
Children may also present with irritability, decreased appetite, or drooling. Chronic tonsillitis can lead to persistent discomfort and recurrent infections.
Causes
Tonsillitis is primarily caused by infectious agents:
- Viral infections: Adenovirus, rhinovirus, influenza, Epstein-Barr virus (mononucleosis), and coronavirus
- Bacterial infections: Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and less commonly Haemophilus influenzae
- Fungal infections: Rarely, in immunocompromised individuals
- Environmental factors: Exposure to infected individuals, crowded living conditions, and seasonal viral outbreaks
The infection triggers immune response, leading to inflammation, redness, swelling, and discomfort.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase susceptibility to tonsillitis:
- Age between 5–15 years (common in children)
- Frequent exposure to viruses or bacteria in schools or daycare centers
- Weakened immune system due to chronic illness or medications
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, which irritates the throat
- Poor oral hygiene, increasing bacterial colonization
- History of recurrent infections or chronic adenoid enlargement
Complications
While most cases resolve without severe issues, tonsillitis can lead to complications, particularly if bacterial and untreated:
- Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy): Painful pus-filled swelling near the tonsil requiring drainage
- Rheumatic fever: Post-streptococcal autoimmune reaction affecting the heart, joints, and skin
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis: Kidney inflammation following bacterial infection
- Chronic tonsillitis: Persistent inflammation causing ongoing discomfort
- Obstructive sleep issues: Enlarged tonsils can lead to snoring or sleep apnea
- Spread of infection: Rarely, infection may extend to surrounding tissues or bloodstream (sepsis)
Early diagnosis and treatment in South Korea prevent these complications and improve patient outcomes.
Prevention
Preventing tonsillitis focuses on reducing exposure to infectious agents and supporting immune health:
- Maintain good hand hygiene and avoid close contact with infected individuals
- Avoid sharing utensils, drinks, or personal items with infected persons
- Ensure proper nutrition and adequate sleep to support immunity
- Regular dental and oral care to minimize bacterial growth
- Vaccination against influenza and other preventable viral illnesses
- Early medical attention for sore throat or fever to treat bacterial infections promptly
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for tonsillitis, ranging from symptomatic relief to surgical interventions for recurrent or severe cases:
Diagnosis:
- Clinical examination of the throat and tonsils
- Rapid antigen detection tests for Group A streptococcus
- Throat culture for definitive bacterial identification
- Blood tests in recurrent or severe infections
- Imaging in cases of suspected abscess formation
Medical Treatments:
- Symptomatic relief: Analgesics, antipyretics, throat lozenges, and hydration
- Antibiotics: Penicillin or amoxicillin for bacterial tonsillitis
- Antiviral therapy: In rare viral cases requiring specialized treatment
- Corticosteroids: Occasionally used to reduce severe swelling and pain
Surgical Treatments:
- Tonsillectomy: Indicated for recurrent, chronic, or severe tonsillitis, or for complications such as abscess
- Minimally invasive tonsillectomy techniques are widely available in Korea, ensuring faster recovery and reduced post-operative pain
Rehabilitation and Support:
- Post-treatment care with hydration, soft diet, and pain management
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing and prevent recurrence
- Patient education on hygiene, nutrition, and lifestyle modifications
- Management of associated sleep or airway issues if tonsil enlargement was present
Korean ENT specialists provide individualized care plans, combining medical, surgical, and supportive therapies to ensure rapid recovery and reduce the likelihood of recurrent infections.