Overview
Adenoid Hypertrophy refers to the abnormal enlargement of the adenoids—lymphatic tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity. While adenoids play a role in immune defense during early childhood, their enlargement can obstruct normal breathing, cause sleep disturbances, and lead to recurrent ear and sinus infections.
What is Adenoid Hypertrophy?
Adenoid Hypertrophy is the pathological enlargement of the adenoid tissue, often seen in children between the ages of 3 and 7. The adenoids are part of the immune system and help fight infections, but as children grow, this tissue typically shrinks. In some cases, however, the adenoids become persistently enlarged, leading to airway obstruction and other complications.
Symptoms
The symptoms of adenoid hypertrophy are usually related to upper airway obstruction and include:
- Persistent nasal congestion or blockage
- Mouth breathing (especially during sleep)
- Snoring or noisy breathing during sleep
- Sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep)
- Frequent ear infections or fluid buildup (otitis media with effusion)
- Chronic sinus infections
- Nasal-sounding speech
- Difficulty swallowing in severe cases
Causes
Common causes and contributing factors include:
- Repeated upper respiratory infections
- Allergies
- Chronic sinusitis
- Exposure to irritants (such as secondhand smoke)
- Genetic predisposition to enlarged lymphoid tissue
Risk Factors
Children are more commonly affected due to their naturally larger adenoid size and developing immune systems. Risk factors include:
- Age: Most common in children aged 3–7
- Frequent infections: Especially respiratory or ear infections
- Environmental exposure: Tobacco smoke, pollution, or allergens
- Allergic conditions: Allergic rhinitis or asthma
- Family history: Enlarged tonsils or adenoids
Complications
If untreated, adenoid hypertrophy may lead to:
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Recurrent ear infections and hearing loss
- Speech delays or articulation problems
- Chronic mouth breathing (can affect facial development)
- Behavioral issues and poor concentration due to poor sleep quality
Prevention
While not always preventable, you can reduce the risk of adenoid problems by:
- Ensuring good hygiene to prevent frequent infections
- Limiting exposure to allergens and irritants
- Managing allergies effectively
- Avoiding secondhand smoke exposure
- Seeking prompt treatment for sinus or ear infections
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and complications:
1. Observation
- Mild cases may resolve as the child grows older.
- Monitoring without immediate intervention is often appropriate.
2. Medications
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays to reduce inflammation
- Antihistamines for allergy-related swelling
- Antibiotics for associated infections
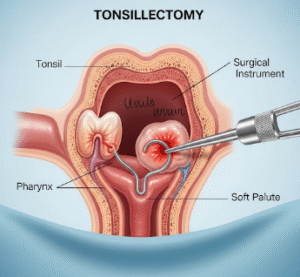
3. Surgical Removal (Adenoidectomy)
- Recommended in persistent or severe cases, especially when:
- Sleep apnea is present
- Chronic ear infections occur
- Breathing or speech is significantly affected
- Often done along with tonsillectomy if both tissues are enlarged