Overview
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a common digestive disorder where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. This reflux can lead to symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation. GERD affects people worldwide, and South Korea offers advanced diagnostic and treatment options to manage this chronic condition effectively.
What is GERD?
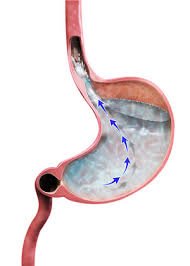
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach, weakens or relaxes inappropriately. This allows acidic stomach contents to flow back (reflux) into the esophagus, leading to inflammation and symptoms. Chronic GERD can cause complications such as esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, and increased risk of esophageal cancer.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of GERD include:
- Frequent heartburn (burning sensation behind the breastbone)
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic cough or throat clearing
- Hoarseness or sore throat
- Chest pain, especially when lying down
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
Causes
- Dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
- Hiatal hernia, where part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm
- Delayed stomach emptying
- Obesity increasing abdominal pressure
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Certain foods and medications that relax the LES
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Consumption of fatty or spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol
- Certain medications (e.g., antihistamines, calcium channel blockers)
- Hiatal hernia
- Age (more common in adults over 40)
Complications
- Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)
- Esophageal ulcers and bleeding
- Strictures (narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue)
- Barrett’s esophagus (pre-cancerous changes in esophageal lining)
- Increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid foods and drinks that trigger reflux
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid lying down within 2-3 hours after eating
- Elevate the head of the bed
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for GERD through modern medical centers equipped with the latest diagnostic and therapeutic technologies:
- Diagnosis
- Upper endoscopy to examine esophageal lining
- 24-hour pH monitoring to measure acid reflux
- Esophageal manometry to evaluate LES function
- Medications
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce acid production
- H2 receptor blockers for mild cases
- Antacids for immediate symptom relief
- Prokinetics to improve stomach emptying
- Lifestyle and Dietary Management
- Personalized diet plans to avoid reflux triggers
- Weight management programs
- Smoking cessation support
- Surgical Treatment
- Nissen fundoplication (laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery) for severe or medication-resistant GERD
- Newer endoscopic procedures to strengthen LES
- Follow-Up and Monitoring
- Regular endoscopic surveillance for patients with Barrett’s esophagus
- Ongoing symptom management and adjustment of treatment