Overview
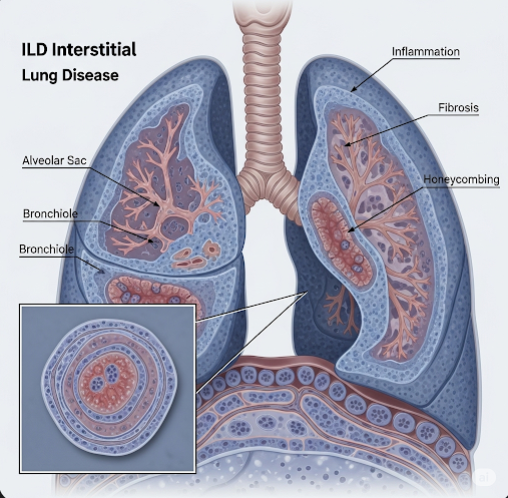
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) refers to a broad group of disorders characterized by progressive scarring and inflammation of the lung’s interstitium — the tissue and space around the air sacs (alveoli). This damage impairs the lungs’ ability to transfer oxygen into the bloodstream, leading to symptoms such as persistent cough, breathlessness, and fatigue. ILD is not a single disease but a collection of over 200 different lung conditions, each with varied causes and patterns of progression. In Korea, advances in pulmonology have improved diagnosis and treatment, making specialized care for ILD more accessible.
What is Interstitial Lung Disease?
Interstitial Lung Disease encompasses a set of chronic lung disorders that cause inflammation and fibrosis (thickening or scarring) of the lung interstitium. This interstitium is a delicate network of tissue surrounding the alveoli where oxygen exchange occurs. When affected by ILD, the lung tissue becomes stiff and less elastic, resulting in impaired lung function.
ILDs can be idiopathic (unknown cause), related to environmental exposures, autoimmune diseases, or drug reactions. Common forms include idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), and sarcoidosis. The disease course can vary widely—from slowly progressive to rapidly fatal—making early diagnosis critical.
Symptoms
The symptoms of ILD often develop gradually and may initially be mild, which can delay diagnosis. Typical symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea): Usually worsens with exertion and progresses over time.
- Dry, persistent cough: Often nonproductive and persistent.
- Fatigue and weakness: Due to decreased oxygenation.
- Chest discomfort or pain: Less common, but may occur.
- Clubbing of fingers: In advanced cases, where fingertips enlarge due to chronic low oxygen.
- Unexplained weight loss: Occasionally present in severe cases.
Because symptoms are nonspecific, ILD is sometimes mistaken for other lung or heart conditions early on.
Causes
The exact cause of many ILDs remains unknown, especially in idiopathic forms. However, several known causes and associations include:
- Environmental and occupational exposures: Long-term inhalation of harmful substances like asbestos, silica dust, coal dust, or bird proteins can trigger ILD.
- Autoimmune and connective tissue diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, and lupus may involve the lungs.
- Medications: Certain drugs (chemotherapy agents, antibiotics like nitrofurantoin, anti-inflammatory drugs) have lung toxicity potential.
- Radiation therapy: Lung damage may follow radiation treatment to the chest.
- Genetics: Some familial cases of ILD suggest a hereditary predisposition.
- Infections: Chronic infections can occasionally cause lung scarring.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing ILD:
- Age: Most common in adults between 50 and 70 years.
- Gender: Some types are more frequent in men.
- Smoking: Strongly linked to certain ILDs such as IPF.
- Occupational exposure: Jobs involving exposure to dust, chemicals, or fumes.
- Underlying autoimmune diseases: Having diseases like rheumatoid arthritis increases risk.
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of ILD or pulmonary fibrosis.
- Geographical location: Some ILDs have higher prevalence in specific regions.
Complications
If left untreated or diagnosed late, ILD can lead to serious complications:
- Respiratory failure: Progressive lung scarring can reduce oxygen exchange, causing chronic hypoxia.
- Pulmonary hypertension: High blood pressure in lung arteries due to increased resistance.
- Cor pulmonale: Right-sided heart failure caused by lung disease.
- Acute exacerbations: Sudden worsening episodes that can be life-threatening.
- Infections: Patients are more vulnerable to lung infections.
- Lung cancer: Some ILDs increase risk of lung cancer.
Prevention
While prevention depends largely on the underlying cause, general strategies include:
- Avoiding exposure: Use protective equipment when working with dust, chemicals, or fumes.
- Smoking cessation: Essential to reduce lung damage risk.
- Managing autoimmune diseases: Early and effective control may reduce lung involvement.
- Regular health checkups: Especially for those at occupational or genetic risk.
- Vaccinations: Influenza and pneumococcal vaccines to prevent respiratory infections.
- Medication review: Avoid drugs known for lung toxicity when possible.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea has developed advanced medical expertise in diagnosing and managing ILD, with specialized pulmonary centers and research institutions.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Diagnosis usually involves high-resolution CT scans, pulmonary function tests, bronchoscopy with lung biopsy if needed, and blood tests to identify causes. Korean hospitals offer cutting-edge imaging and diagnostic labs to ensure precise assessment.
- Medications:
- Antifibrotic agents: Drugs like pirfenidone and nintedanib are widely used in Korea for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis to slow disease progression.
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants: For inflammatory ILDs linked to autoimmune diseases or hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
- Oxygen therapy: Provided to improve oxygen levels in advanced cases.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Comprehensive programs in Korean hospitals include exercise training, breathing techniques, and education to improve quality of life.
- Lung Transplantation: For eligible patients with advanced, progressive disease, Korea offers lung transplantation at major medical centers with good outcomes.
- Clinical Trials: Korea actively participates in global ILD research, providing access to novel therapies and cutting-edge treatments.
- Multidisciplinary Care: Patients benefit from coordinated care involving pulmonologists, rheumatologists, radiologists, and specialized nurses.