Overview
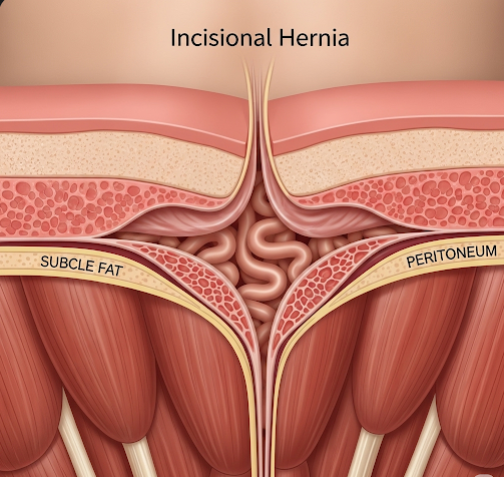
An incisional hernia is a type of hernia that occurs at the site of a previous surgical incision in the abdominal wall. It develops when the muscles and tissues around the surgical wound weaken or fail to heal properly, allowing internal organs or fatty tissue to protrude through the weakened area. Incisional hernias can cause discomfort, pain, and complications such as bowel obstruction or strangulation if untreated. In Korea, advanced surgical techniques and postoperative care protocols help effectively diagnose and manage incisional hernias, improving patient recovery and reducing recurrence.
What is an Incisional Hernia?
An incisional hernia forms when abdominal contents push through a defect or weakness at the site of a previous surgical scar. This type of hernia can develop weeks, months, or even years after the original surgery, depending on factors affecting wound healing and abdominal pressure.
Symptoms
- Bulge or swelling near or at the site of a prior surgical incision
- Discomfort or pain, especially when lifting, coughing, or straining
- Feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdomen
- Redness or tenderness around the hernia site in some cases
- Symptoms of bowel obstruction such as nausea, vomiting, and constipation if hernia contents become trapped
Causes
- Inadequate healing or poor surgical technique during abdominal surgery
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure from coughing, heavy lifting, or obesity
- Infection at the surgical site impairing wound healing
- Poor nutrition or chronic diseases affecting tissue repair
- Repeated abdominal surgeries or emergency procedures
Risk Factors
- Older age with reduced tissue elasticity
- Obesity and smoking impairing wound healing
- Diabetes or other chronic illnesses
- Use of steroids or immunosuppressive drugs
- Postoperative wound infections
Complications
- Enlargement of the hernia causing increased discomfort
- Bowel obstruction due to trapped intestines
- Strangulation leading to tissue death and emergency surgery
- Recurrence after surgical repair
Prevention
- Proper surgical technique and wound care during initial surgery
- Managing risk factors like obesity and smoking cessation
- Avoiding heavy lifting and straining during recovery
- Timely treatment of wound infections
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination noting bulge or tenderness at incision site
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan to assess hernia size and contents
- Evaluation for signs of complications like bowel obstruction
Medical Treatments
- Observation for small, asymptomatic hernias
- Pain management and lifestyle modifications to reduce intra-abdominal pressure
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Elective hernia repair surgery recommended for symptomatic or enlarging hernias
- Open or laparoscopic hernia repair techniques using mesh reinforcement to strengthen the abdominal wall
- Component separation technique for large or complex hernias
- Use of biologic mesh in contaminated surgical fields to reduce infection risk
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative care including wound monitoring and pain control
- Gradual return to physical activity with guidance from healthcare providers
- Nutritional support to promote healing
- Regular follow-up to detect recurrence
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Abdominal Surgery Department
- Samsung Medical Center – Hernia Repair Clinic
- Asan Medical Center – Minimally Invasive Surgery Unit
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Digestive Surgery Department