Overview
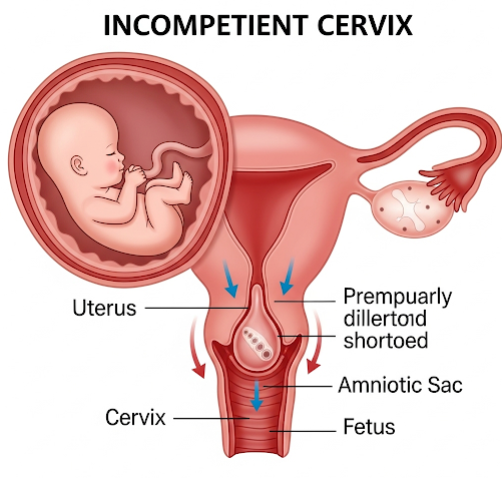
An incompetent cervix, also known as cervical insufficiency, is a condition where the cervix—the lower part of the uterus—weakens and dilates prematurely during pregnancy without contractions. This can lead to miscarriage or preterm birth, often in the second trimester. In Korea, maternal-fetal medicine specialists offer advanced diagnostic tools and interventions, such as cervical cerclage, to manage incompetent cervix and improve pregnancy outcomes.
What is Incompetent Cervix?
An incompetent cervix refers to the painless opening (dilation) and shortening (effacement) of the cervix before the pregnancy reaches full term, usually without labor contractions. The weakened cervix cannot maintain the pregnancy, increasing the risk of premature delivery or pregnancy loss.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic in early stages
- Vaginal spotting or discharge
- Pelvic pressure or mild cramping
- Premature rupture of membranes in some cases
- Later signs include cervical dilation detected during routine ultrasound or examination
Causes
- Congenital weakness or structural abnormalities of the cervix
- Previous cervical surgery such as cone biopsy or LEEP
- Trauma to the cervix from childbirth or instrumentation
- Multiple prior pregnancies or cervical lacerations
- Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES) in utero (rare)
Risk Factors
- History of second-trimester pregnancy losses or preterm births
- Cervical trauma or surgery
- Uterine anomalies
- Multiple gestations (twins or more)
- Short cervical length measured by ultrasound during pregnancy
Complications
- Miscarriage or preterm birth
- Infection from premature rupture of membranes
- Neonatal complications related to prematurity
Prevention
- Early prenatal care with cervical length monitoring via transvaginal ultrasound
- Avoiding activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure in high-risk patients
- Timely interventions to reinforce the cervix
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Transvaginal ultrasound to measure cervical length and detect funneling
- History evaluation of pregnancy losses and cervical procedures
- Physical pelvic examination if needed
Medical Treatments
- Bed rest and activity modification in some cases (though evidence varies)
- Progesterone supplementation to reduce preterm birth risk
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Cervical cerclage: a surgical procedure placing stitches around the cervix to keep it closed
- Types include:
- McDonald cerclage (most common)
- Shirodkar cerclage (higher placement)
- Transabdominal cerclage (for severe cases)
- Timing typically between 12-14 weeks of pregnancy
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular ultrasound monitoring after cerclage
- Education on signs of preterm labor and infection
- Psychological support to manage pregnancy anxiety
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Maternal-Fetal Medicine
- Samsung Medical Center – Obstetrics and Gynecology Department
- Asan Medical Center – High-Risk Pregnancy Clinic
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Women’s Health Center