Overview
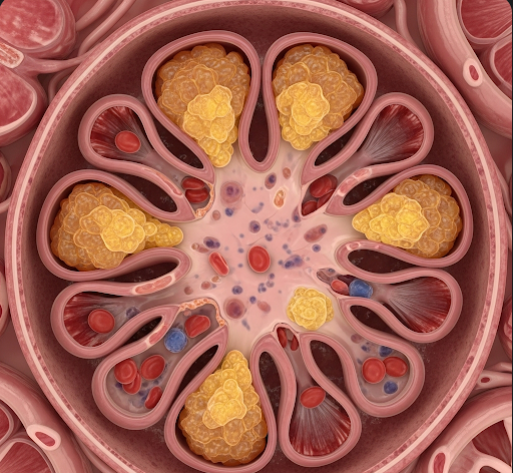
IgA Nephropathy, also known as Berger’s disease, is a kidney disorder characterized by the deposition of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies in the glomeruli, the filtering units of the kidneys. This accumulation causes inflammation, which can lead to impaired kidney function over time. IgA Nephropathy is one of the most common causes of glomerulonephritis worldwide, including in Korea, where specialized nephrology centers offer advanced diagnostic tools and tailored treatment plans to manage the condition and slow its progression.
What is IgA Nephropathy?
IgA Nephropathy is a form of chronic kidney disease caused by abnormal immune responses leading to IgA deposits in the kidneys. These deposits trigger inflammation and damage, impairing the kidneys’ ability to filter blood effectively. The disease varies widely in severity, ranging from mild cases with little impact to progressive kidney failure.
Symptoms
- Presence of blood in the urine (hematuria), often visible during or after infections
- Proteinuria (excess protein in urine)
- Swelling in the hands, feet, or face (edema)
- High blood pressure
- Fatigue and weakness in advanced stages
- In some cases, asymptomatic until kidney function declines
Causes
- Abnormal immune response producing defective IgA antibodies
- Genetic predisposition, with certain populations more affected
- Triggered or worsened by infections, particularly of the respiratory tract
Risk Factors
- Family history of IgA Nephropathy
- Male gender (more commonly affected)
- Age between teens and 30s
- Recurrent respiratory infections
Complications
- Progressive kidney damage leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Hypertension worsening kidney function
- Nephrotic syndrome (severe protein loss in urine)
- End-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis or transplantation
Prevention
While the root cause is not preventable, risk of progression can be reduced by:
- Controlling blood pressure effectively
- Treating infections promptly
- Avoiding medications harmful to kidneys
- Regular monitoring of kidney function
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Urinalysis to detect blood and protein in urine
- Blood tests to assess kidney function (creatinine, eGFR)
- Kidney biopsy to confirm IgA deposits and evaluate damage
- Imaging studies like ultrasound to assess kidney size and structure
Medical Treatments
- Blood pressure control – ACE inhibitors or ARBs to reduce proteinuria and protect kidneys
- Immunosuppressive therapy – Corticosteroids or other agents in selected cases with severe inflammation
- Fish oil supplements – Sometimes used for anti-inflammatory effects
- Supportive care – Dietary salt restriction, fluid management
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Kidney transplantation in cases of ESRD
- Dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis) for kidney failure
Rehabilitation and Support
- Lifestyle counseling for diet and exercise to support kidney health
- Regular nephrology follow-up for monitoring disease progression
- Patient education on recognizing symptoms of worsening kidney function
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital – Nephrology Department
- Asan Medical Center – Kidney and Hypertension Clinic
- Samsung Medical Center – Division of Nephrology
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Renal and Transplant Center