Overview
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid or bile flows back into the esophagus, irritating its lining. While occasional acid reflux is common, GERD involves frequent symptoms that can significantly affect daily life. In Korea, advancements in diagnostics and minimally invasive treatments have made managing GERD more effective.
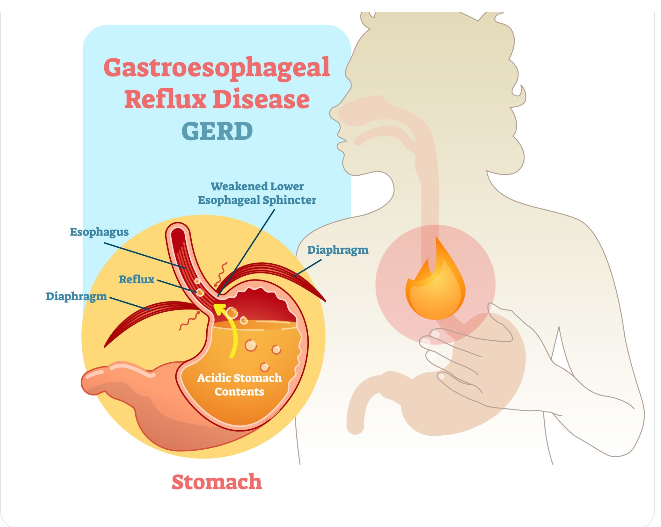
What is GERD?
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) — the muscle between the esophagus and stomach — does not close properly or opens too often, allowing acid to escape into the esophagus. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, ulcers, or other complications.
Symptoms
- Persistent heartburn (especially after meals or at night)
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic cough, hoarseness, or sore throat
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
Causes
- Weak or relaxed LES muscle
- Hiatal hernia
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Certain foods (spicy, fatty, acidic) and beverages (coffee, carbonated drinks)
- Medications that relax the LES
Risk Factors
- Being overweight or obese
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Family history of GERD
- Chronic stress
- High-fat or highly processed diets
Complications
- Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)
- Esophageal strictures (narrowing)
- Barrett’s esophagus (precancerous changes)
- Esophageal cancer
- Chronic respiratory issues (asthma, bronchitis)
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid lying down immediately after meals
- Limit trigger foods and drinks
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Elevate the head of the bed during sleep
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, GERD treatment is highly specialized, combining lifestyle guidance, medications, and advanced procedures:
- Lifestyle Counseling: Diet modification programs with nutritionists experienced in reflux management.
- Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 receptor blockers, and prokinetics.
- Endoscopic Treatments: Endoscopic radiofrequency therapy (Stretta) or endoscopic fundoplication for non-invasive LES strengthening.
- Surgical Interventions: Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication or LINX device implantation for severe, unresponsive cases.
- Comprehensive Care Centers: University hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide multidisciplinary GERD clinics with gastroenterologists, surgeons, and dietitians.