Overview
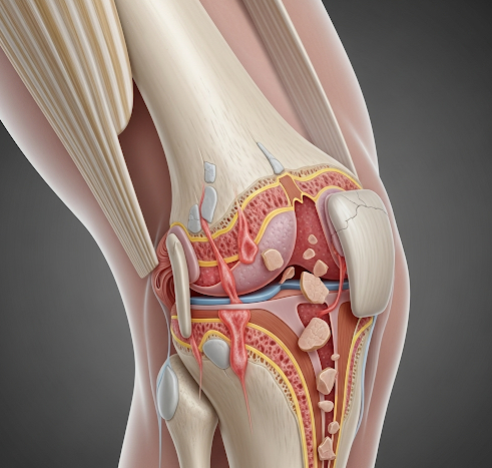
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. It is one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, particularly affecting older adults. In Korea, advanced orthopedic care, rehabilitation services, and innovative surgical techniques such as minimally invasive knee replacement are widely available to manage symptoms and improve patient quality of life.
What Is Knee Osteoarthritis?
Knee osteoarthritis is a chronic condition where the protective cartilage cushioning the ends of bones in the knee joint deteriorates over time. This cartilage loss causes bones to rub against each other, resulting in inflammation, pain, and joint damage. OA can affect one or both knees and typically progresses slowly but can lead to severe functional limitations if untreated. It is influenced by mechanical stress, age-related changes, and biochemical factors affecting joint tissues.
Symptoms
- Persistent knee pain worsening with activity and improving with rest
- Joint stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity or in the morning
- Swelling and tenderness around the knee
- Reduced range of motion and difficulty fully bending or straightening the knee
- A sensation of grinding, clicking, or popping during movement
- Weakness or instability, causing a feeling of the knee “giving way”
- Deformities such as bowing or knock-knee appearance in advanced stages
Causes
- Age-related wear and tear leading to cartilage degradation
- Previous knee injuries such as fractures, ligament tears, or meniscal damage
- Repetitive stress or overuse from occupations or sports
- Obesity increasing mechanical load on the knee joint
- Genetic predisposition influencing cartilage and bone metabolism
- Inflammatory processes and biochemical changes within the joint
Risk Factors
- Age over 50 years, with prevalence increasing with age
- Female gender, especially postmenopausal women
- Obesity and excess body weight
- History of knee trauma or surgery
- Occupations involving repetitive kneeling, squatting, or heavy lifting
- Genetic and family history of osteoarthritis
Complications
- Chronic pain affecting daily activities and sleep quality
- Progressive joint deformity and loss of function
- Reduced mobility leading to muscle weakness and decreased physical fitness
- Psychological effects including depression and social isolation due to disability
- Increased risk of falls and secondary injuries
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Regular low-impact exercise to strengthen muscles supporting the knee
- Avoiding repetitive high-impact activities or injury risks
- Early treatment of knee injuries to prevent long-term damage
- Balanced diet rich in nutrients supporting joint health, including omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean medical centers offer a full spectrum of treatment for knee osteoarthritis, combining conservative measures, pharmacotherapy, and advanced surgical options:
- Conservative Management:
- Physical therapy focusing on strengthening, flexibility, and pain relief
- Use of assistive devices such as braces or walking aids to improve joint stability
- Lifestyle modifications including weight loss and activity adjustments
- Medications:
- Analgesics such as acetaminophen for mild pain
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Intra-articular injections including corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid to improve joint lubrication and reduce symptoms
- Surgical Treatments:
- Arthroscopic surgery for meniscal repair or cartilage debridement in select cases
- Osteotomy to realign bones and redistribute weight in younger patients with localized damage
- Partial or total knee replacement (arthroplasty) for advanced osteoarthritis with severe pain and functional loss
- Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted knee replacement techniques available in Korea enhance precision and recovery
- Rehabilitation and Postoperative Care:
- Comprehensive rehab programs to restore strength, range of motion, and function
- Pain management and patient education to facilitate recovery and long-term joint health
Korea’s orthopedic expertise, cutting-edge technology, and patient-centered care ensure effective management of knee osteoarthritis, improving mobility and quality of life for patients.