Overview
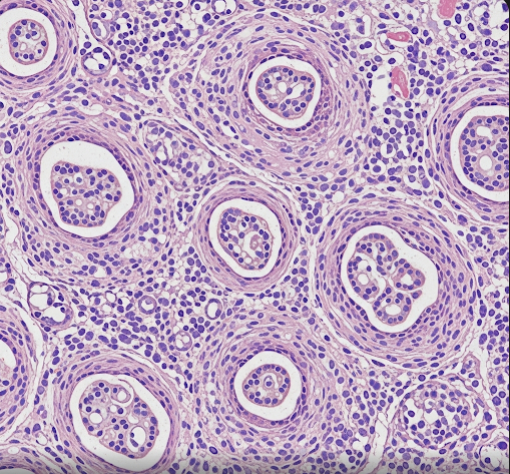
Rosai-Dorfman Disease (RDD), also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare benign disorder characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of histiocytes (a type of immune cell) primarily within lymph nodes but can affect other organs. It often causes painless, massive lymph node enlargement and systemic symptoms. In Korea, hematology and pathology specialists provide accurate diagnosis and multidisciplinary management for RDD patients.
What is Rosai-Dorfman Disease?
Rosai-Dorfman Disease is a rare disorder involving the abnormal proliferation of histiocytes, typically within lymph nodes, leading to painless swelling. While it most commonly affects the cervical lymph nodes, extranodal involvement of skin, respiratory tract, or other organs can occur. The cause is unclear, and the disease usually follows a benign but sometimes chronic course.
Symptoms
- Painless, massive enlargement of lymph nodes, especially in the neck
- Fever and night sweats
- Weight loss and fatigue
- Enlarged lymph nodes in other regions (axillary, inguinal)
- Possible involvement of skin, respiratory tract, eyes, or central nervous system causing related symptoms
Causes
- Unknown etiology, possibly related to immune dysregulation or infections
- No confirmed infectious or genetic cause
Risk Factors
- Usually affects children and young adults
- No specific environmental or genetic risk factors identified
Complications
- Compression of adjacent structures by enlarged lymph nodes
- Organ dysfunction if extranodal sites are involved
- Rarely, disease may become chronic or recurrent
Prevention
- No known prevention due to unclear cause
- Early diagnosis and monitoring to manage symptoms and complications
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hematology and oncology centers provide tailored treatment for Rosai-Dorfman Disease:
- Observation: Many cases resolve spontaneously and may only require monitoring.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and lymph node size in symptomatic cases.
- Surgery: Removal of affected lymph nodes or masses causing symptoms.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: In refractory or widespread disease.
- Radiation or Chemotherapy: Rarely used for severe or organ-threatening disease.
- Supportive Care: Management of symptoms and complications as needed.