Overview
Rh factor, also known as the Rhesus factor, is an important protein found on the surface of red blood cells. It plays a critical role in blood compatibility, especially during pregnancy and blood transfusions. Understanding Rh factor is vital to prevent complications such as hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). In Korea, advanced prenatal screening and blood typing ensure safe pregnancies and transfusions by managing Rh incompatibility effectively.
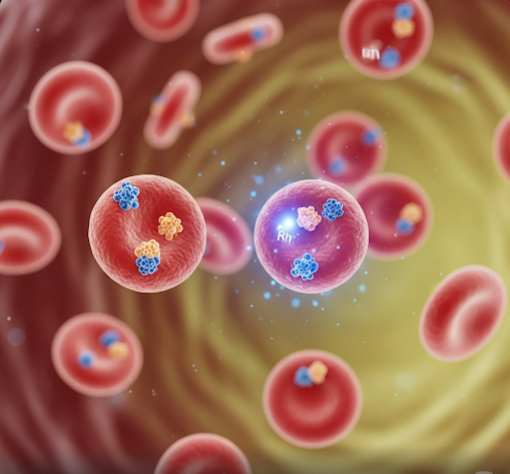
What is Rh Factor?
Rh factor is a protein that can be present (Rh-positive) or absent (Rh-negative) on red blood cells. Most people are Rh-positive. Problems arise when an Rh-negative mother carries an Rh-positive fetus, potentially leading to immune reactions that affect the baby’s health.
Symptoms
Rh factor itself does not cause symptoms, but Rh incompatibility can lead to:
- Jaundice in the newborn
- Anemia
- Swelling (hydrops fetalis)
- In severe cases, stillbirth
Causes
- Inherited genetic trait determining the presence or absence of Rh protein
- Rh incompatibility occurs when the mother’s immune system attacks Rh-positive fetal red blood cells
Risk Factors
- Rh-negative mother with an Rh-positive partner
- Previous pregnancy with an Rh-positive baby
- Blood transfusions with Rh-positive blood in an Rh-negative individual
Complications
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), causing destruction of fetal red blood cells
- Anemia and jaundice in the newborn
- Miscarriage or stillbirth in severe cases
Prevention
- Routine prenatal Rh factor screening for all pregnant women
- Administration of Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) injections to Rh-negative mothers during and after pregnancy to prevent antibody formation
- Careful blood typing and cross-matching before transfusions
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean healthcare centers provide comprehensive management of Rh factor-related issues:
- Prenatal Screening: Early and repeated blood tests to determine Rh status and antibody presence.
- Rh Immunoglobulin Therapy: Given to Rh-negative pregnant women at risk to prevent sensitization.
- Monitoring: Regular ultrasound and fetal monitoring in pregnancies complicated by Rh incompatibility.
- Treatment of Newborns: Phototherapy, blood transfusions, or exchange transfusions for affected infants.
- Blood Transfusion Services: Strict protocols to ensure Rh compatibility during transfusions.