Overview
Rickets is a childhood bone disorder caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate, leading to soft and weakened bones. It results in bone deformities, growth disturbances, and skeletal pain. In Korea, early diagnosis through pediatric screenings and effective nutritional and medical treatments help prevent and manage rickets, ensuring healthy bone development.
What is Rickets?
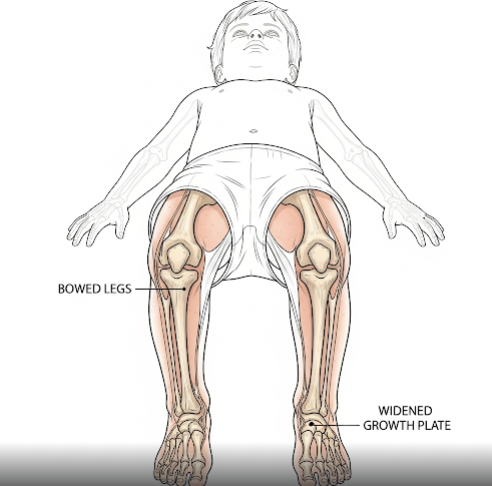
Rickets occurs when there is inadequate mineralization of the growing bones in children, primarily due to vitamin D deficiency or problems with calcium and phosphate metabolism. This leads to soft, pliable bones that can become deformed or fractured easily.
Symptoms
- Delayed growth and short stature
- Bone pain or tenderness, especially in the legs, pelvis, and spine
- Skeletal deformities such as bowed legs (genu varum), knock knees (genu valgum), and thickened wrists or ankles
- Delayed motor milestones (e.g., walking)
- Dental problems such as delayed tooth eruption
- Muscle weakness
Causes
- Vitamin D deficiency from inadequate sunlight exposure or poor diet
- Malabsorption disorders affecting vitamin D or minerals
- Genetic disorders affecting vitamin D metabolism or phosphate regulation
- Chronic kidney or liver diseases
Risk Factors
- Infants and young children, especially exclusively breastfed babies without supplementation
- Limited sun exposure due to lifestyle or geographic location
- Poor dietary intake of vitamin D and calcium
- Certain medical conditions affecting nutrient absorption
Complications
- Bone deformities and fractures
- Growth retardation
- Dental problems
- Increased risk of respiratory infections due to weakened chest muscles
Prevention
- Adequate exposure to sunlight
- Vitamin D and calcium supplementation for infants and children at risk
- Balanced diet rich in vitamin D and calcium
- Regular pediatric check-ups and growth monitoring
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean pediatric healthcare providers offer comprehensive management for rickets:
- Vitamin D Supplementation: Oral vitamin D3 supplements tailored to deficiency severity.
- Calcium and Phosphate Therapy: Nutritional support and supplements as needed.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions: Addressing malabsorption or metabolic disorders.
- Monitoring: Regular assessment of bone growth, mineral levels, and radiographic evaluation.
- Education: Guidance for parents on nutrition, sun exposure, and prevention strategies.