Overview
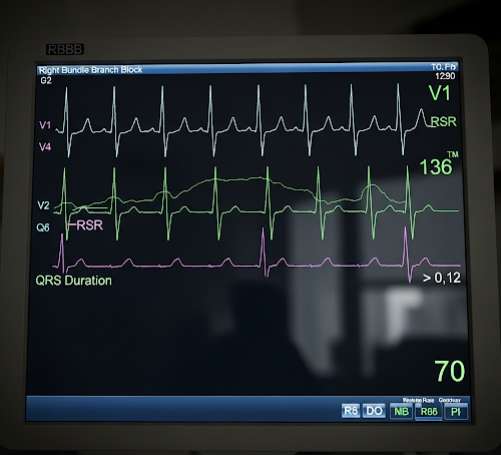
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB) is a condition in which the electrical conduction pathway along the right bundle branch of the heart’s electrical system is delayed or blocked. This affects the timing of right ventricular contraction but is often benign. In Korea, advanced cardiology diagnostics allow for accurate detection and monitoring of RBBB, ensuring appropriate management based on underlying causes.
What is Right Bundle Branch Block?
RBBB occurs when the electrical impulses traveling through the right bundle branch of the heart’s conduction system are slowed or blocked. This results in a delay in the electrical activation of the right ventricle, visible on an electrocardiogram (ECG) as a distinctive pattern. RBBB can be either complete or incomplete.
Symptoms
- Most individuals with RBBB are asymptomatic
- Sometimes palpitations or mild chest discomfort
- Rarely, symptoms related to underlying heart conditions (e.g., shortness of breath, fatigue)
Causes
- Normal variant in healthy individuals
- Heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, myocarditis, or cardiomyopathy
- Pulmonary embolism or pulmonary hypertension
- Congenital heart defects
- After heart surgery or trauma to the heart
Risk Factors
- Aging
- Heart disease or structural heart abnormalities
- History of heart attack or inflammation
- Pulmonary diseases causing right heart strain
Complications
- Usually none in isolated RBBB
- May indicate underlying heart disease requiring treatment
- In rare cases, progression to more serious conduction abnormalities or arrhythmias
Prevention
- Managing risk factors for cardiovascular disease
- Regular cardiac evaluations if underlying heart disease is present
- Avoidance of smoking, hypertension, and other modifiable risks
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean cardiology centers offer comprehensive evaluation and management of RBBB:
- Diagnostic Testing: Electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiography, stress testing, and cardiac MRI as needed.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up for asymptomatic individuals to watch for changes or progression.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: Treatment of coronary artery disease, hypertension, or pulmonary disorders if present.
- Pacemaker: Rarely required unless associated with symptomatic heart block or arrhythmias.
- Lifestyle Advice: Heart-healthy diet, exercise, and risk factor control.