Overview
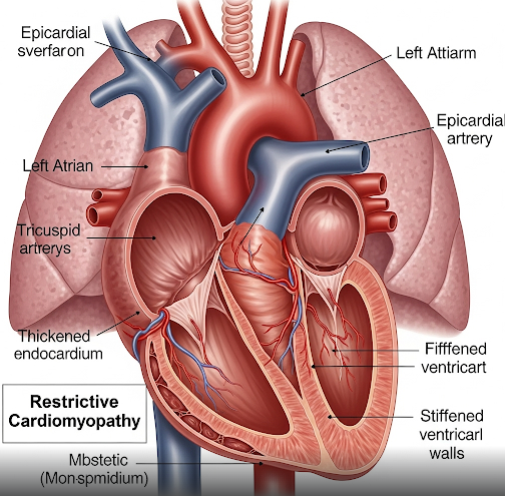
Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is a rare heart muscle disorder where the walls of the ventricles become stiff, limiting the heart’s ability to fill properly during diastole. While the pumping function may remain normal, the impaired filling leads to symptoms of heart failure. In Korea, cutting-edge cardiac imaging, genetic testing, and specialized treatment centers provide accurate diagnosis and advanced management for RCM patients.
What is Restrictive Cardiomyopathy?
RCM is a condition where the heart muscle loses its elasticity without becoming thickened (as in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) or weakened (as in dilated cardiomyopathy). This stiffness prevents the ventricles from expanding enough to accommodate blood returning from the body and lungs, leading to reduced cardiac output and congestion. It can be idiopathic or secondary to conditions like amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, or endomyocardial fibrosis.
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath (especially during exertion)
- Fatigue and reduced exercise tolerance
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Chest discomfort
- Difficulty breathing when lying flat (orthopnea)
Causes
- Infiltrative diseases (e.g., amyloidosis, sarcoidosis)
- Genetic mutations affecting heart muscle proteins
- Post-radiation therapy changes
- Endomyocardial fibrosis
- Idiopathic (unknown cause)
Risk Factors
- Family history of cardiomyopathy
- Autoimmune or inflammatory diseases
- History of cancer treatments involving chest radiation
- Chronic systemic conditions such as amyloidosis
Complications
- Congestive heart failure
- Atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias
- Blood clots (due to sluggish blood flow)
- Sudden cardiac death in severe cases
- Progressive exercise intolerance and disability
Prevention
- Early detection and management of underlying conditions (e.g., amyloidosis)
- Genetic screening for at-risk families
- Regular heart check-ups for those with systemic diseases linked to RCM
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Echocardiography with Doppler imaging
- Cardiac MRI to detect myocardial stiffness and infiltration
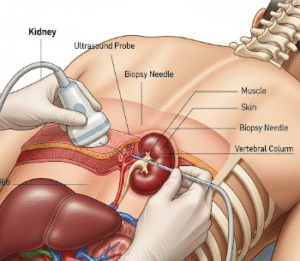
- Endomyocardial biopsy for definitive diagnosis in certain cases
- Blood tests for biomarkers and genetic analysis
- Nuclear imaging for amyloidosis detection
Medical Treatments
- Medications to manage heart failure symptoms (diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors)
- Drugs to control arrhythmias and prevent clot formation (anticoagulants)
- Disease-specific therapies for amyloidosis or sarcoidosis
Interventional & Surgical Treatments
- Pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) for rhythm management
- Heart transplantation in end-stage cases unresponsive to medical therapy
Advanced Therapies
- Targeted drug therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis (e.g., tafamidis)
- Immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory causes
- Participation in clinical trials for novel cardiomyopathy treatments
Rehabilitation and Support
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs in Korean hospitals to improve stamina and quality of life
- Nutrition counseling for fluid and sodium management
- Psychological support for patients coping with chronic heart disease
- Ongoing follow-up with cardiology specialists
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea for Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – Leading in advanced cardiac imaging and heart failure care
- Seoul National University Hospital – Expertise in rare cardiomyopathies and transplant surgery
- Samsung Medical Center – Strong multidisciplinary team for amyloidosis and infiltrative heart diseases
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Comprehensive cardiology and genetic testing services
- Korea University Anam Hospital – Specialized in cardiac rehabilitation and advanced heart imaging