Overview
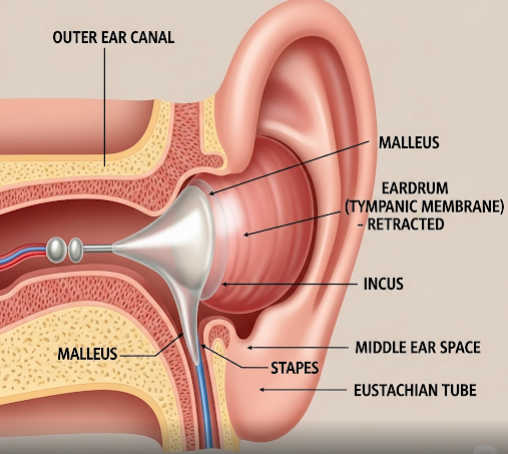
A retracted eardrum is a condition where the eardrum (tympanic membrane) is pulled inward toward the middle ear space, often due to pressure imbalances. This can cause discomfort, hearing problems, and increase the risk of middle ear infections. In Korea, advanced ENT diagnostics and treatments are available to effectively manage and resolve this condition.
What is Retracted Eardrum?
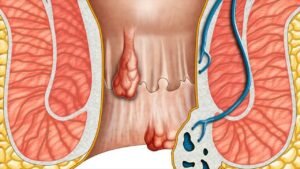
A retracted eardrum occurs when negative pressure in the middle ear pulls the eardrum inward, causing it to appear sunken or concave. This usually results from dysfunction of the Eustachian tube, which regulates pressure between the middle ear and the throat.
Symptoms
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Mild to moderate hearing loss
- Ear discomfort or pain
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ear)
- Sometimes no symptoms in early stages
Causes
- Eustachian tube dysfunction causing poor ventilation of the middle ear
- Upper respiratory infections or allergies causing inflammation
- Chronic sinus infections
- Sudden changes in altitude or pressure (e.g., flying, diving)
- Chronic nasal congestion or blockage
Risk Factors
- Frequent upper respiratory infections
- Allergic rhinitis or sinusitis
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Anatomical abnormalities of the Eustachian tube
- Children, due to shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes
Complications
- Persistent hearing loss if untreated
- Middle ear infections (otitis media)
- Cholesteatoma formation (abnormal skin growth in the middle ear)
- Tympanic membrane perforation
- Chronic middle ear disease
Prevention
- Managing allergies and upper respiratory infections promptly
- Avoiding smoking and irritants
- Regular ENT check-ups for individuals with recurrent ear problems
- Treating nasal congestion and sinus issues effectively
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean ENT clinics offer modern diagnostic and therapeutic options for retracted eardrum:
- Diagnostic Evaluation: Otoscopy, tympanometry, and audiometry to assess eardrum status and hearing function.
- Medical Management: Decongestants, nasal steroids, and antihistamines to reduce inflammation and improve Eustachian tube function.
- Autoinflation Therapy: Techniques to help open the Eustachian tube and equalize pressure.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Myringotomy with or without tube insertion: Small incision in the eardrum to relieve pressure and insert a ventilation tube if needed.
- Tympanoplasty: Surgical repair of the eardrum in severe or chronic cases.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring to prevent recurrence and complications.