Overview
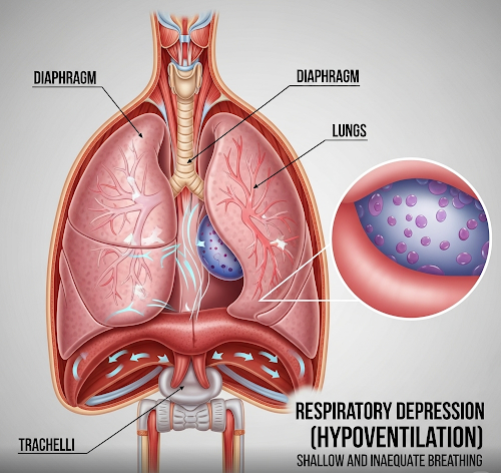
Respiratory depression, also known as hypoventilation, is a serious medical condition characterized by inadequate ventilation leading to increased carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels in the blood and reduced oxygen levels. It can result from various causes affecting the respiratory center, muscles, or airway. Korea provides advanced critical care, diagnostic tools, and tailored treatments to manage respiratory depression effectively.
What is Respiratory Depression (Hypoventilation)?
Respiratory depression occurs when the breathing rate and depth are insufficient to meet the body’s oxygen demands and remove CO₂ efficiently. This leads to respiratory acidosis and can cause life-threatening complications if untreated.
Symptoms
- Slow or shallow breathing
- Confusion or drowsiness
- Headache
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of skin)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Loss of consciousness in severe cases
Causes
- Drug overdose (e.g., opioids, sedatives)
- Brainstem injury or neurological disorders
- Severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
- Sleep apnea
- Muscle diseases affecting respiratory muscles
Risk Factors
- Use of central nervous system depressants
- Neurological conditions such as stroke or brain injury
- Obesity and respiratory disorders
- Chronic lung diseases
Complications
- Respiratory failure
- Hypoxia leading to organ damage
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Coma or death if untreated
Prevention
- Careful use and monitoring of sedative or opioid medications
- Early treatment of neurological and respiratory diseases
- Weight management and treatment of sleep apnea
- Regular medical check-ups in at-risk populations
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis to assess oxygen and CO₂ levels
- Pulmonary function tests
- Polysomnography for sleep-related breathing disorders
- Neurological evaluation and imaging
Medical Treatments
- Reversal agents for drug overdose (e.g., naloxone for opioids)
- Supplemental oxygen therapy
- Non-invasive ventilation (e.g., CPAP or BiPAP)
- Treatment of underlying causes such as COPD or obesity hypoventilation
Interventional & Surgical Treatments
- Tracheostomy for prolonged mechanical ventilation
- Surgical treatment of obstructive sleep apnea (e.g., UPPP)
Advanced Therapies
- Use of advanced ventilators with tailored respiratory support
- Multidisciplinary care involving pulmonologists, neurologists, and intensivists
Rehabilitation and Support
- Respiratory therapy and muscle strengthening exercises
- Patient education on medication safety and lifestyle changes
- Monitoring and management of chronic conditions
- Psychological support and counseling
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea for Respiratory Depression
- Seoul National University Hospital – Leading critical care and pulmonary services
- Asan Medical Center – Advanced respiratory and neurological care
- Samsung Medical Center – Expertise in mechanical ventilation and sleep disorders
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Comprehensive respiratory and critical care
- Korea University Anam Hospital – Specialized in neuromuscular and pulmonary diseases