Overview
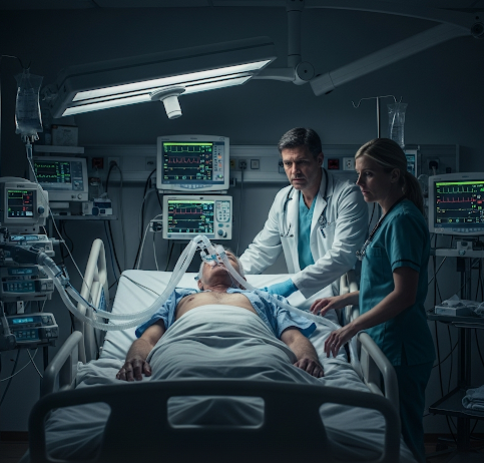
Respiratory failure is a life-threatening condition where the lungs fail to adequately oxygenate the blood or remove carbon dioxide, resulting in low oxygen levels (hypoxemia), high carbon dioxide levels (hypercapnia), or both. It can be acute or chronic and requires urgent medical attention. Korea is recognized for its advanced intensive care units (ICUs), cutting-edge respiratory therapies, and expert multidisciplinary teams to manage respiratory failure effectively.
What is Respiratory Failure?
Respiratory failure occurs when the respiratory system cannot maintain proper gas exchange, leading to insufficient oxygen delivery to tissues and/or inadequate removal of carbon dioxide from the blood. It can result from lung diseases, neurological conditions, or other systemic problems affecting breathing.
Symptoms
- Severe shortness of breath
- Rapid or shallow breathing
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of lips, face, or extremities)
- Confusion, agitation, or loss of consciousness
- Fatigue and inability to speak in full sentences
- Chest pain or palpitations
Causes
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations
- Pneumonia or severe lung infections
- Pulmonary embolism
- Neuromuscular diseases affecting breathing muscles
- Drug overdose causing respiratory depression
Risk Factors
- Chronic lung diseases (COPD, asthma, fibrosis)
- Neurological disorders (stroke, ALS)
- Smoking and environmental pollutants
- Severe infections
- Use of sedatives or narcotics
Complications
- Multi-organ failure due to hypoxia
- Cardiac arrest
- Permanent lung damage
- Death if untreated or improperly managed
Prevention
- Timely treatment of lung infections and chronic diseases
- Avoidance of smoking and exposure to pollutants
- Regular medical follow-up for at-risk patients
- Vaccinations to prevent respiratory infections
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis for oxygen and carbon dioxide levels
- Chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests
- Continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation and vital signs
- Bronchoscopy or sputum analysis to identify infections
Medical Treatments
- Oxygen therapy and ventilatory support
- Medications such as bronchodilators, antibiotics, and corticosteroids
- Treatment of underlying causes (e.g., antibiotics for pneumonia)
- Sedation and pain control in ventilated patients
Interventional & Surgical Treatments
- Mechanical ventilation via endotracheal tube or tracheostomy
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for severe cases
- Surgical intervention for underlying causes like pulmonary embolism
Advanced Therapies
- Use of non-invasive ventilation (NIV) techniques
- Pulmonary rehabilitation post-recovery
- Advanced ICU monitoring and care protocols
- Multidisciplinary teams including pulmonologists, intensivists, and respiratory therapists
Rehabilitation and Support
- Respiratory therapy to restore lung function
- Nutritional support to aid recovery
- Psychological counseling for critically ill patients
- Long-term follow-up to monitor lung health
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea for Respiratory Failure
- Seoul National University Hospital – State-of-the-art ICU and respiratory care
- Asan Medical Center – Leading center for critical care and pulmonary medicine
- Samsung Medical Center – Expertise in advanced respiratory therapies and ECMO
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Comprehensive management of acute and chronic respiratory failure
- Korea University Anam Hospital – Specialized multidisciplinary care for respiratory disorders