Overview
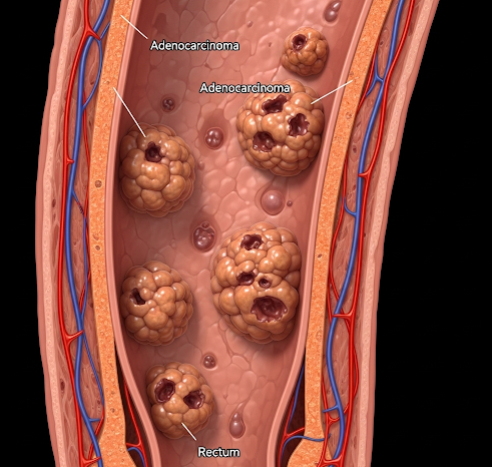
Rectal cancer is a malignant tumor arising in the rectum, the final segment of the large intestine. It is a common type of colorectal cancer and requires timely diagnosis and treatment to improve outcomes.
What Is Rectal Cancer?
Rectal cancer develops when abnormal cells in the rectal lining grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can invade surrounding tissues and spread (metastasize). It often starts as benign polyps that gradually become cancerous.
Symptoms
- Rectal bleeding or blood in stool
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, narrowing of stool)
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Sensation of incomplete bowel evacuation
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and anemia
- Mucus discharge from the rectum
Causes
- Genetic mutations leading to abnormal cell growth
- Progression from adenomatous polyps
- Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease)
- Lifestyle factors such as diet, smoking, and alcohol use
Risk Factors
- Age over 50 years
- Family history of colorectal cancer or polyps
- Personal history of inflammatory bowel disease
- Sedentary lifestyle and obesity
- Diet high in red and processed meats
- Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption
Complications
- Local tumor invasion causing bowel obstruction
- Metastasis to liver, lungs, or lymph nodes
- Bleeding and anemia
- Infection or perforation of the bowel
Prevention
- Regular screening colonoscopy especially after age 50
- Healthy diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables
- Regular physical activity
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol
- Managing inflammatory bowel diseases effectively
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced multidisciplinary care for rectal cancer:
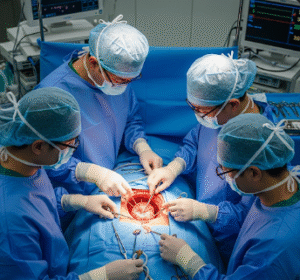
- Surgery: Total mesorectal excision or minimally invasive techniques to remove tumors.
- Radiation Therapy: Preoperative or postoperative radiotherapy to reduce recurrence risk.
- Chemotherapy: Used alone or with radiation for advanced stages or metastatic disease.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs targeting specific molecular pathways in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: For select cases with specific genetic markers.
- Rehabilitation and Support: Nutritional support, stoma care, and psychological counseling.
- Advanced Diagnostics: High-resolution imaging, endoscopy, and molecular testing for precise staging and personalized treatment.
Korean cancer centers emphasize early detection, personalized treatment plans, and comprehensive supportive care to improve survival and quality of life.