Overview
Lupus, or Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and damage. It can affect multiple organs including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and brain.
What Is Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus)?
SLE is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of autoantibodies that attack healthy cells and tissues. Its symptoms vary widely and can range from mild to life-threatening. It primarily affects women of childbearing age but can occur in any gender or age.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and fever
- Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
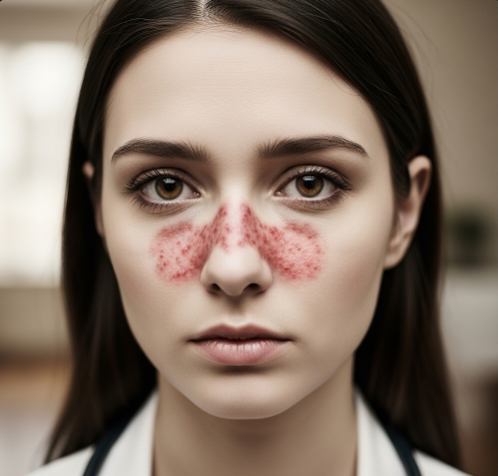
- Skin rashes, including a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose
- Photosensitivity (sensitivity to sunlight)
- Mouth or nose ulcers
- Hair loss
- Kidney problems (lupus nephritis)
- Chest pain due to inflammation of the lining of the heart or lungs
- Neurological symptoms like headaches, seizures, or cognitive dysfunction
Causes
- Exact cause unknown; believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors
- Immune system dysregulation leading to autoantibody production
- Triggers include infections, sunlight exposure, certain medications, and stress
Risk Factors
- Female gender (90% of cases)
- Age between 15 and 45 years
- Family history of autoimmune diseases
- Certain ethnic backgrounds (higher prevalence in African, Hispanic, and Asian populations)
Complications
- Kidney failure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Stroke
- Severe infections due to immune suppression
- Lung inflammation (pleuritis)
- Blood clotting disorders
Prevention
- Avoiding known triggers such as excessive sun exposure
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing stress
- Regular monitoring and early treatment of symptoms
- Avoiding certain medications that can induce lupus-like symptoms
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers specialized care for lupus with a multidisciplinary approach:
- Medications: Immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, antimalarials (e.g., hydroxychloroquine), and biologics to control inflammation and immune response.
- Regular Monitoring: Blood tests, urine tests, and imaging to monitor organ involvement.
- Lifestyle Support: Sun protection, diet, and exercise guidance.
- Patient Education: Support groups and counseling to manage chronic illness.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Autoantibody profiling and kidney biopsy when needed.
- Integrated Care: Collaboration between rheumatologists, nephrologists, dermatologists, and other specialists.
Korean medical centers provide comprehensive lupus management focusing on improving quality of life and preventing organ damage.