Overview
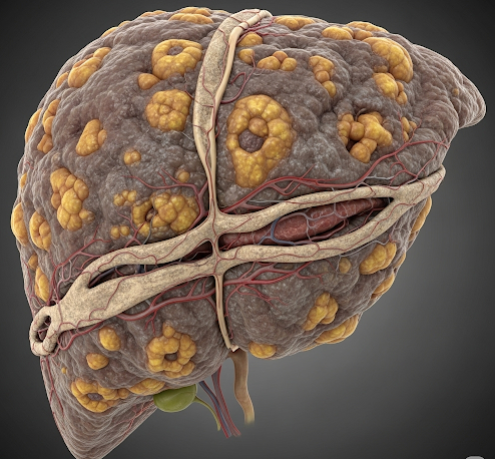
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic, progressive condition characterized by scarring (fibrosis) of liver tissue that impairs liver function. It results from long-term liver damage caused by various diseases and can lead to life-threatening complications if untreated.
What Is Liver Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is the advanced stage of liver fibrosis where normal liver architecture is replaced by scar tissue. This scarring disrupts blood flow through the liver and diminishes its ability to perform vital functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and bile production.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Abdominal swelling (ascites)
- Swelling of legs (edema)
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Itchy skin
- Confusion or difficulty thinking (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Enlarged spleen
- Spider-like blood vessels on skin
Causes
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection
- Long-term excessive alcohol consumption
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) related to obesity and diabetes
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Bile duct diseases (primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis)
- Genetic disorders (hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease)
Risk Factors
- Chronic viral hepatitis infection
- Alcohol abuse
- Metabolic syndrome and obesity
- Family history of liver disease
- Exposure to toxins or certain medications
Complications
- Portal hypertension causing varices and bleeding
- Ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- Hepatic encephalopathy leading to coma
- Liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma)
- Kidney dysfunction (hepatorenal syndrome)
- Bone disease and malnutrition
Prevention
- Vaccination for hepatitis B and treatment of hepatitis C
- Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining completely
- Maintaining a healthy weight and controlling diabetes
- Regular screening for liver disease in high-risk groups
- Avoiding exposure to liver toxins and unsafe medications
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea provides advanced, multidisciplinary care for liver cirrhosis:
- Medical Management: Medications to manage symptoms, control complications (e.g., diuretics for ascites, beta-blockers for variceal bleeding prevention).
- Lifestyle Modifications: Alcohol cessation, diet changes, and exercise guidance.
- Monitoring and Screening: Regular imaging and blood tests to detect liver cancer early.
- Endoscopic Treatments: Band ligation or sclerotherapy for variceal bleeding.
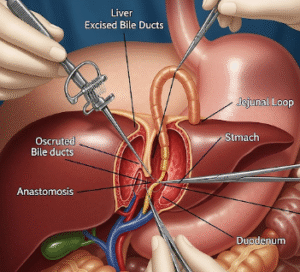
- Liver Transplantation: Curative option for end-stage cirrhosis with specialized transplant centers in Korea.
- Supportive Care: Nutritional support, management of hepatic encephalopathy, and psychosocial counseling.
Korean healthcare centers combine expert hepatologists, advanced diagnostics, and comprehensive treatment programs to improve outcomes and quality of life for patients with liver cirrhosis.