Overview
Vitamin B deficiency refers to the lack of one or more B vitamins essential for energy metabolism, nervous system function, and red blood cell production. Since the B vitamins include a group of several related nutrients (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12), deficiency can affect multiple body systems, leading to symptoms ranging from fatigue to neurological problems. South Korea offers advanced diagnostic and treatment options to address various forms of vitamin B deficiency.
What is Vitamin B Deficiency?
Vitamin B deficiency occurs when the body lacks adequate amounts of one or more B vitamins. Each B vitamin has unique roles; for example, B12 and folate (B9) are vital for red blood cell formation and neurological health, while B1 (thiamine) is crucial for energy production. Deficiency may result from poor dietary intake, malabsorption, certain medical conditions, or increased physiological demands.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on which B vitamin is deficient but may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
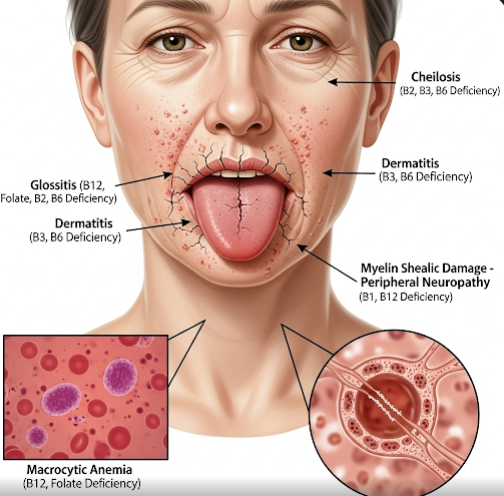
- Anemia (pale skin, shortness of breath)
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Difficulty walking or balance problems
- Memory issues or confusion
- Mouth sores or glossitis (inflamed tongue)
- Mood changes such as depression or irritability
Causes
- Inadequate dietary intake, especially in strict vegetarians or elderly individuals
- Malabsorption conditions like celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or pernicious anemia
- Alcoholism, which impairs vitamin absorption
- Certain medications interfering with vitamin metabolism
- Increased requirements during pregnancy, lactation, or illness
Risk Factors
- Vegetarian or vegan diets lacking animal products (risk for B12 deficiency)
- Older adults with reduced absorption capacity
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases
- Alcohol abuse
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Use of medications like metformin or proton pump inhibitors
Complications
- Neurological damage including peripheral neuropathy and cognitive decline
- Severe anemia leading to heart complications
- Increased risk of birth defects (neural tube defects) with folate deficiency
- Impaired immune function
- Mental health disorders
Prevention
- Balanced diet including sources of B vitamins such as meat, dairy, eggs, legumes, and fortified cereals
- Vitamin B12 supplementation for vegetarians, vegans, and at-risk groups
- Screening and early treatment in populations with malabsorption or chronic diseases
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Monitoring medication effects on vitamin levels
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for vitamin B deficiency, including:
- Vitamin supplementation – Oral or injectable B complex vitamins tailored to the specific deficiency
- Dietary counseling – Guidance to improve intake of B vitamin-rich foods
- Management of underlying causes – Treatment for malabsorption disorders or medication adjustments
- Regular monitoring – Blood tests to track vitamin levels and treatment response
- Public health education – Awareness programs emphasizing the importance of balanced nutrition