Overview
Overflow incontinence is a type of urinary incontinence characterized by the involuntary leakage of urine due to an overfilled bladder that cannot empty properly. This condition often results from bladder outlet obstruction or weakened bladder muscles. In Korea, urologists and specialists offer comprehensive diagnostic and treatment options to manage overflow incontinence and improve patient quality of life.
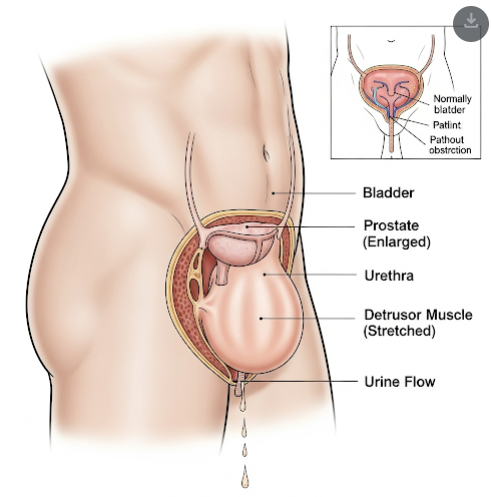
What is Overflow Incontinence?
Overflow incontinence occurs when the bladder is unable to empty fully, leading to frequent dribbling or continuous leakage of small amounts of urine. It differs from other forms of incontinence by being caused primarily by mechanical or functional blockage or poor bladder muscle contractility.
Symptoms
Symptoms of overflow incontinence include:
- Constant dribbling of urine or weak urine stream
- Frequent urination or feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- Difficulty starting urination
- Urinary retention or sensation of bladder fullness
- Possible urinary tract infections due to stagnant urine
Causes
Common causes of overflow incontinence include:
- Bladder outlet obstruction from enlarged prostate (in men)
- Urethral stricture or pelvic organ prolapse (in women)
- Neurogenic bladder due to spinal cord injury or diabetes
- Weakened detrusor muscle from aging or neurological disease
- Certain medications affecting bladder function
Risk Factors
Risk factors for overflow incontinence include:
- Advanced age
- Male gender, especially with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Diabetes mellitus and neurological disorders
- Previous pelvic surgeries or radiation therapy
- Use of certain medications like anticholinergics or alpha-adrenergic agonists
Complications
If untreated, overflow incontinence can lead to:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Kidney damage from chronic urinary retention
- Skin irritation and breakdown due to constant leakage
- Reduced quality of life and social embarrassment
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- Regular medical check-ups for prostate and bladder health
- Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes effectively
- Avoiding medications that impair bladder function when possible
- Early intervention for urinary symptoms
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment of overflow incontinence in Korea includes:
- Medications: Alpha-blockers for prostate enlargement, drugs to improve bladder contractility
- Catheterization: Intermittent or indwelling catheter use to relieve retention
- Surgical interventions: Procedures to remove obstruction such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- Pelvic floor rehabilitation: Exercises and biofeedback for bladder control
- Neuromodulation therapies: Electrical stimulation techniques for neurogenic bladder cases
Korean urology centers utilize advanced diagnostic tools like urodynamic studies and imaging to tailor effective, patient-specific treatments for overflow incontinence.