Overview
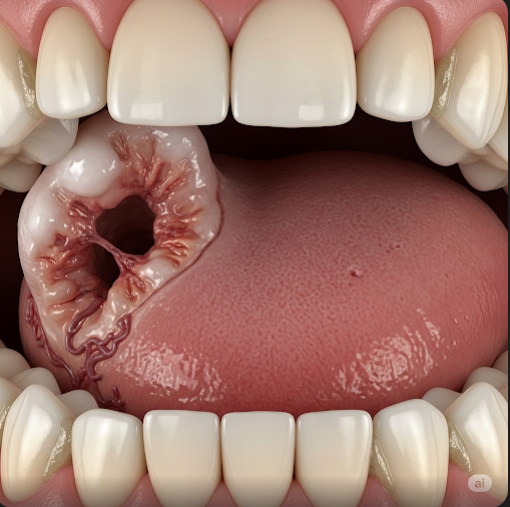
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth or throat. It can appear on the lips, tongue, gums, inner lining of the cheeks, roof of the mouth, or under the tongue. This type of cancer can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. Like many other cancers, it often begins as a painless lesion or sore and can progress quickly. Oral cancer is more common in people over the age of 40, but lifestyle choices and other risk factors can influence its development.
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer refers to malignant growths that occur in any part of the mouth. It belongs to a larger group of cancers called head and neck cancers. Most oral cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, which originate in the thin, flat cells lining the mouth and lips. This condition can interfere with essential functions such as speaking, eating, and swallowing, especially as it advances. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Symptoms
- A sore in the mouth that doesn’t heal
- Persistent pain in the mouth
- A lump or thickening in the cheek
- White or red patches on the gums, tongue, tonsil, or lining of the mouth
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Jaw pain or stiffness
- Numbness of the tongue or other areas of the mouth
- Voice changes or persistent sore throat
- Unexplained weight loss
Causes
Oral cancer is caused by mutations in the DNA of cells in the mouth, leading them to grow uncontrollably and form tumors. The exact cause is often multifactorial, including lifestyle habits and environmental exposures. Major contributing causes include:
- Tobacco use (cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco)
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Excessive sun exposure (especially for lip cancer)
- Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation from rough teeth or dentures
- Family history of cancer
Risk Factors
- Smoking or using any form of tobacco
- Regular consumption of alcohol, especially in combination with tobacco
- HPV infection, particularly strain HPV-16
- Age over 40
- Male gender (oral cancer is more common in men)
- Poor diet lacking fruits and vegetables
- Weak immune system
- Prolonged sun exposure (for lip cancer)
- History of oral cancer or other cancers
Complications
If not treated early, oral cancer can lead to severe complications such as:
- Spread to nearby structures like lymph nodes, jawbone, or throat
- Difficulty in speaking, chewing, or swallowing
- Facial disfigurement from surgery or tumor growth
- Recurrence of cancer in other areas of the body
- Psychological impact such as depression or anxiety
- Malnutrition due to eating difficulties
- Reduced quality of life and social challenges
Prevention
- Avoid all tobacco products
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption
- Protect lips from sun exposure using lip balm with SPF
- Maintain good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Get vaccinated against HPV
- Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals or irritants
- Perform regular self-examinations and report any changes to a healthcare provider
Treatment Option in Korea
South Korea is recognized for its advanced medical infrastructure and cutting-edge cancer treatment options. For oral cancer, treatment plans typically involve a multidisciplinary approach:
- Surgical treatment: Removal of the tumor and possibly affected lymph nodes. Minimally invasive and reconstructive surgeries are available at specialized cancer centers.
- Radiation therapy: Targeted radiation to kill cancer cells, often used after surgery or as a standalone treatment in early-stage cancers.
- Chemotherapy: Used in advanced cases or alongside radiation to destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that target specific cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- Rehabilitation and support: Speech therapy, nutrition counseling, and psychological support services are provided to aid recovery.
Top hospitals in Korea such as Severance Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Asan Medical Center offer personalized cancer care, English-speaking staff, and modern diagnostic tools. Medical tourism support is also available for international patients.