Overview
Oral health problems and diabetes are closely connected, creating a two-way relationship where each condition can affect the other. People with diabetes are more likely to experience oral health issues such as gum disease, dry mouth, and infections. On the other hand, untreated oral infections can make it harder to control blood sugar levels. Understanding this relationship is essential for managing diabetes effectively and maintaining good oral hygiene.
What is the Connection Between Oral Health and Diabetes?
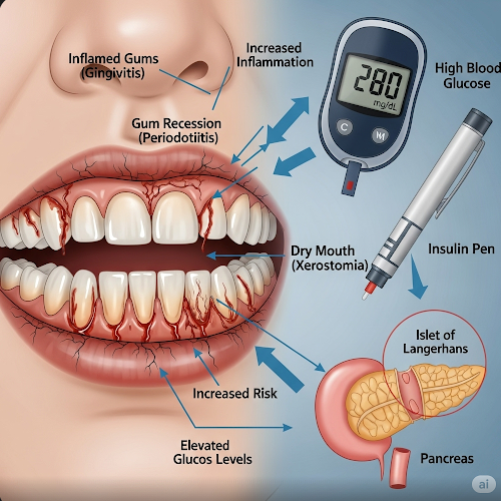
Diabetes reduces the body’s ability to fight off infection and affects blood flow, including to the gums and other oral tissues. High blood sugar levels can lead to an increased risk of developing oral health issues like periodontal disease. In turn, these oral problems can lead to increased inflammation, which can elevate blood sugar levels and make diabetes management more difficult. Proper dental care is a crucial part of comprehensive diabetes management.
Symptoms
Common oral health problems experienced by people with diabetes may include:
- Swollen, red, or bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose teeth or changes in bite
- Gum recession or pockets forming between teeth and gums
- Dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Burning sensation in the mouth or tongue
- White patches on the tongue or cheeks (thrush)
- Delayed healing of oral wounds or sores
Causes
The primary cause of oral health issues in people with diabetes is elevated blood glucose, which impairs immune function and increases the risk of bacterial infections. Other causes include:
- Poorly managed diabetes
- Decreased saliva production
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- High levels of plaque buildup
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Wearing ill-fitting dentures
- Frequent infections or inflammation in the body
Risk Factors
- Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes
- Poor glycemic (blood sugar) control
- Smoking or using tobacco
- Infrequent dental visits or poor oral hygiene
- Older age
- Long duration of diabetes
- Obesity or poor diet
- Stress or weakened immune system
Complications
When oral health issues are not addressed in diabetic patients, they can lead to serious complications:
- Advanced periodontal (gum) disease, leading to tooth loss
- Increased difficulty controlling blood sugar
- Greater risk of systemic infections
- Oral thrush or fungal infections
- Dry mouth causing tooth decay and discomfort
- Increased medical expenses and complications related to diabetes management
Prevention
- Maintain good blood sugar control through medication, diet, and lifestyle
- Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Avoid tobacco products in all forms
- Schedule regular dental check-ups (every 6 months or more frequently if advised)
- Inform your dentist that you have diabetes
- Use alcohol-free mouthwash to avoid worsening dry mouth
- Stay hydrated and chew sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva
Treatment Option in Korea
South Korea provides high-quality integrated care for managing diabetes and its associated oral health issues. Patients can access advanced dental clinics and endocrinology departments that work in coordination for comprehensive treatment. Treatment approaches may include:
- Periodontal therapy: Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), and in severe cases, surgical intervention to treat gum disease
- Saliva replacement therapy: For dry mouth, patients may be prescribed artificial saliva or special rinses
- Antifungal treatment: For oral thrush caused by high glucose levels
- Diabetes education: Programs to help patients manage blood sugar and understand how it affects oral health
- Preventive care: Routine dental cleanings, oral screenings, and early intervention for any sign of infection
Top medical institutions such as Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Yonsei University Dental Hospital, and Samsung Medical Center offer multilingual support and customized care plans. These facilities are ideal for international patients seeking world-class treatment and dental services in Korea.