Overview
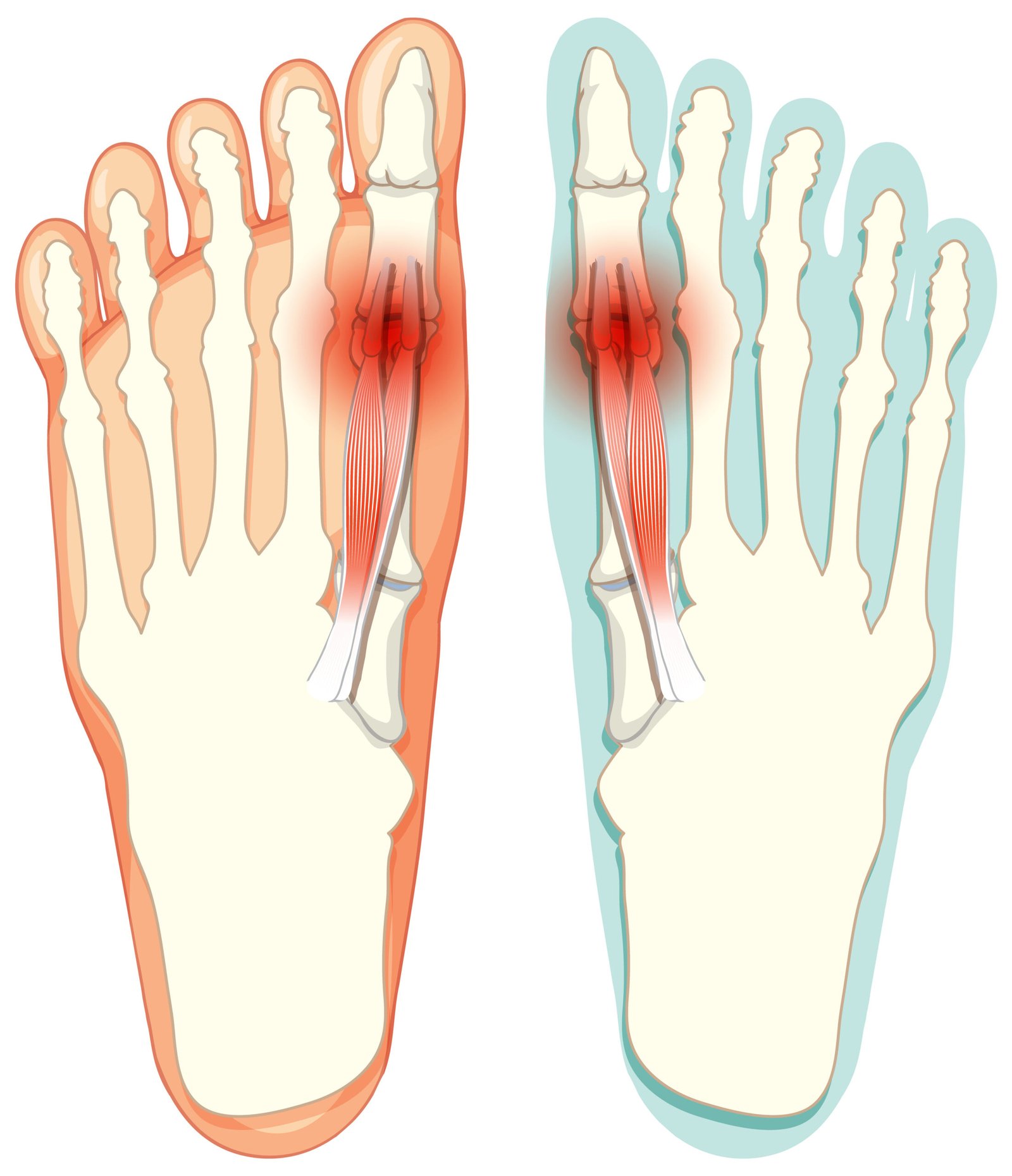
Symmetrical peripheral neuropathy is a condition in which damage to the peripheral nerves affects both sides of the body in a similar pattern. It often begins in the longest nerves—typically in the feet and hands—and can cause numbness, tingling, burning pain, and weakness. This condition can result from various causes, including diabetes, nutritional deficiencies, toxins, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications.
What is Symmetrical Peripheral Neuropathy?
Symmetrical peripheral neuropathy refers to nerve damage that occurs in a mirror-like distribution on both sides of the body, often starting in the extremities. It is the most common pattern of peripheral neuropathy and is sometimes described as a “stocking-glove” pattern because of how symptoms spread. Over time, it can affect mobility, coordination, and quality of life.
Symptoms
- Numbness or tingling in both feet or hands
- Burning or stabbing pain
- Weakness in legs or arms
- Loss of balance and coordination
- Increased sensitivity to touch (allodynia)
- Muscle cramps or twitching
- Reduced reflexes in affected areas
Causes
- Diabetes mellitus (most common cause)
- Chronic alcohol use
- Vitamin deficiencies (B1, B6, B12, E)
- Chronic kidney disease
- Autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Infections (e.g., HIV, hepatitis C)
- Certain chemotherapy or antibiotic drugs
- Exposure to heavy metals or toxins
Risk Factors
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Malnutrition or poor dietary intake
- Chronic kidney or liver disease
- Family history of neuropathy
- Autoimmune or inflammatory conditions
- Prolonged exposure to toxins or certain medications
Complications
- Foot ulcers and infections due to numbness
- Difficulty walking and increased fall risk
- Muscle weakness and wasting
- Chronic pain affecting sleep and daily activities
- Reduced independence in self-care
- Possible permanent nerve damage if untreated
Prevention
- Maintain good blood sugar control in diabetes
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption
- Use protective equipment when working with toxins
- Monitor and manage chronic health conditions
- Get regular foot and hand check-ups if at risk
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, management of symmetrical peripheral neuropathy focuses on treating the underlying cause, controlling symptoms, and preventing complications. Options include:
- Medical evaluation & diagnostics: Nerve conduction studies, blood tests for diabetes, vitamin levels, and autoimmune markers
- Medications:
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Neuropathic pain agents such as pregabalin, duloxetine, or gabapentin
- Vitamin supplementation (e.g., B12 injections)
- Physical therapy & rehabilitation: Exercises to improve strength, balance, and coordination
- Acupuncture & traditional Korean medicine: Sometimes used alongside conventional care for pain relief and nerve stimulation
- Lifestyle modifications: Customized diet plans, alcohol cessation programs, and home safety adjustments to prevent falls
- Diabetic neuropathy care programs: Available in major Korean hospitals, with specialized foot care and nerve health monitoring