Overview
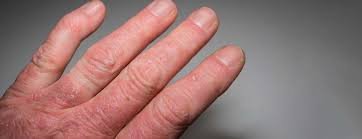
Symmetric polyarthritis is a condition characterized by inflammation affecting the same joints on both sides of the body, such as both wrists, knees, or hands. This pattern of joint involvement is commonly seen in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. The condition often leads to joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and functional limitations, potentially causing long-term joint damage if not managed properly.
What is Symmetric Polyarthritis?
Symmetric polyarthritis refers to arthritis that affects five or more joints in a symmetrical pattern. It is most often associated with chronic inflammatory conditions, especially autoimmune diseases, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues. This symmetry distinguishes it from other forms of arthritis that might affect joints in a random or asymmetrical pattern.
Symptoms
- Pain in the same joints on both sides of the body
- Swelling and warmth in affected joints
- Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes
- Redness over joints
- Reduced range of motion
- Fatigue and general malaise
Causes
- Autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Viral infections (e.g., parvovirus B19, hepatitis)
- Chronic inflammatory diseases (e.g., psoriatic arthritis, scleroderma)
- Metabolic conditions (e.g., gout in rare symmetric cases)
- Genetic predisposition to inflammatory diseases
Risk Factors
- Family history of autoimmune or inflammatory joint diseases
- Female gender (especially for rheumatoid arthritis)
- Age between 30–60 years
- Smoking and other environmental triggers
- Previous viral infections
Complications
- Permanent joint deformity and damage
- Reduced mobility and disability
- Systemic organ involvement in autoimmune diseases (lungs, heart, eyes)
- Chronic pain and decreased quality of life
- Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases due to chronic inflammation
Prevention
- Early diagnosis and treatment of underlying autoimmune conditions
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise
- Avoiding smoking and reducing alcohol consumption
- Protecting joints from repetitive strain
- Following an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids
Treatment Options in Korea
In South Korea, treatment for symmetric polyarthritis focuses on controlling inflammation, preventing joint damage, and improving quality of life through a combination of advanced medical care and lifestyle management:
- Pharmacological treatments:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine
- Biologic agents (e.g., TNF inhibitors, IL-6 blockers) available in leading hospitals
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief
- Corticosteroids for short-term inflammation control
- Rehabilitation & Physical Therapy:
- Specialized physiotherapy programs in Korean rehabilitation centers to maintain joint flexibility and strength
- Hydrotherapy and occupational therapy for joint protection techniques
- Lifestyle and Integrative Medicine:
- Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM) approaches like acupuncture and herbal formulations for symptom relief
- Nutritional counseling focusing on anti-inflammatory foods
- Advanced Care Facilities:
- Hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide multidisciplinary arthritis care, including rheumatology, rehabilitation, and orthopedics.