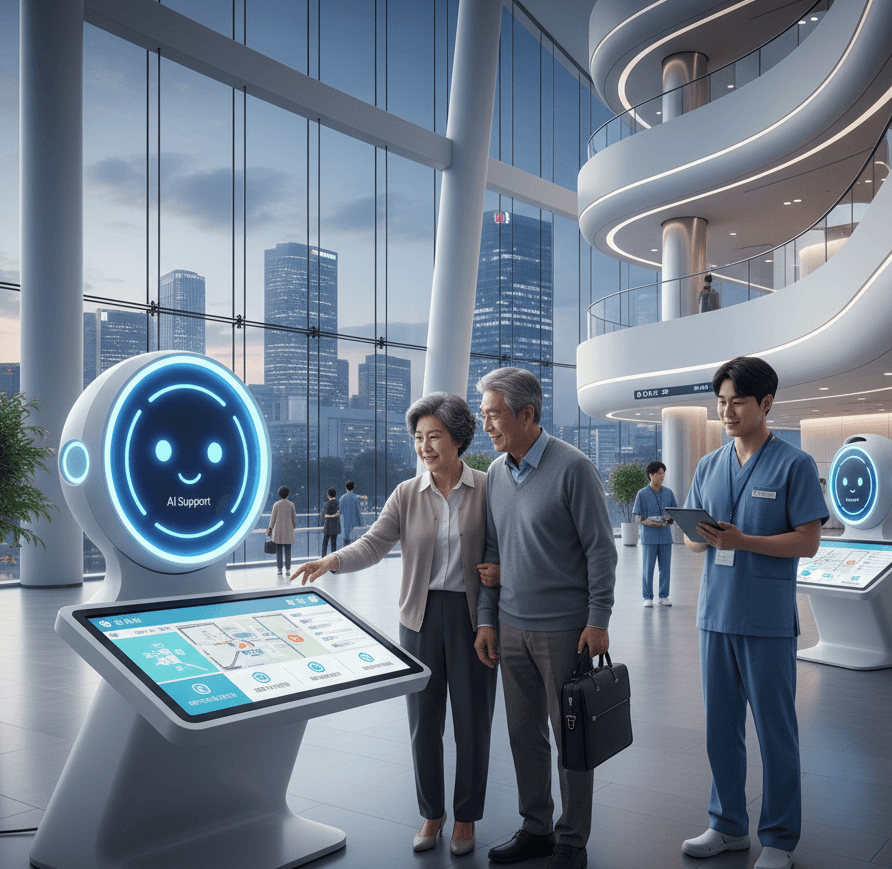
As South Korea rapidly transitions into a super-aged society, loneliness and social isolation among seniors have become pressing concerns. With fewer traditional family caregivers and growing numbers of elderly people living alone, the nation is turning to digital companionship tools — robots, AI apps, and smart devices — to bridge the emotional gap. These technologies are helping older adults stay connected, feel valued, and maintain their independence, marking a new era of human-centered innovation in elder care.
The Growing Need for Companionship
South Korea has one of the world’s fastest-aging populations. Nearly 25% of Koreans will be over 65 by 2030, and more seniors are living independently due to smaller family units and urban migration.
● Loneliness and Mental Health: Many elderly citizens experience social isolation, which can lead to depression, anxiety, or cognitive decline.
● Living Alone: Over 1.8 million seniors in Korea live by themselves — a number projected to keep rising.
● Family Distance: Busy work schedules and urban lifestyles mean that family visits often become infrequent.
Recognizing these challenges, the Korean government and tech sector are developing innovative ways to provide emotional companionship through technology — ensuring that seniors remain connected and cared for, even when human contact is limited.
Government-Led Digital Care Programs
The Ministry of Health and Welfare and local governments are spearheading the introduction of digital companion tools under Korea’s “Smart Care for the Elderly” initiative.
● AI Companion Robots: Government-funded programs distribute AI-based robots to seniors living alone. These robots can hold basic conversations, play music, remind users to take medication, and alert social workers if something seems wrong.
● Remote Monitoring Systems: Devices equipped with sensors track movement, voice activity, and emotional patterns, helping identify loneliness or health risks early.
● Pilot Projects: Municipalities like Seoul, Busan, and Incheon have launched digital companionship pilot projects, providing robots to seniors in welfare housing and evaluating their effects on mood and daily engagement.
● Emergency Connection Services: Some robots and smart speakers automatically connect seniors to 24-hour care centers or family members if they detect distress or inactivity.
These national efforts aim to ensure that technology complements, rather than replaces, human care — blending innovation with compassion.
Popular Digital Companionship Devices in Korea
Several tech companies are now producing AI companions specifically for Korea’s elderly population.
● “Hyodol” Robot: One of Korea’s most successful companion robots, Hyodol resembles a soft doll and speaks with warmth and emotion. It can remember users’ routines, greet them by name, and offer gentle reminders for meals or medicine. Hyodol also tracks voice responses, helping identify signs of loneliness or cognitive decline.
● “Bomy” and “Luvo” Robots: Designed to provide two-way conversation and entertainment, these devices tell stories, play games, and monitor health-related behaviors. They have proven especially popular in nursing homes and senior community centers.
● Smart Speakers and Tablets: Devices like Naver Clova and Kakao Mini are being used as virtual assistants for elderly users, offering weather updates, medication alerts, and news in a friendly, conversational tone.
● AI Pets: Robot pets such as Aibo-style dogs and cats mimic affectionate behaviors — moving, purring, or wagging — which can help reduce stress and feelings of isolation.
These technologies are tailored to Korea’s cultural and linguistic context, allowing elderly users to communicate naturally in Korean and enjoy a sense of companionship that feels genuine.
Integration with Healthcare and Social Services
Digital companionship tools are increasingly linked to Korea’s social welfare and healthcare systems.
● Smart Home Integration: Companion robots connect with IoT sensors and smart home systems that monitor temperature, lighting, and movement, ensuring a safe living environment.
● Healthcare Connectivity: Devices transmit health data — such as voice tone, movement, or sleep patterns — to local health centers, allowing early detection of potential issues.
● Social Worker Networks: AI systems can automatically notify case managers or family members if a senior shows signs of distress or irregular activity.
● Customized Wellness Programs: Some robots deliver guided stretching routines, memory games, and breathing exercises to support both mental and physical health.
This seamless integration allows Korea’s digital care ecosystem to function not only as emotional support but also as a preventive healthcare tool.
Psychological and Social Benefits
Digital companionship tools have shown measurable positive effects on seniors’ mental health and daily engagement.
● Reduced Loneliness: Studies by local universities show that seniors using companion robots report a 20–30% reduction in loneliness scores after three months.
● Improved Emotional Stability: Interaction with AI devices helps regulate mood, reducing anxiety and depression.
● Enhanced Cognitive Function: Memory games and conversational features help stimulate cognitive activity and slow cognitive decline.
● Better Routine Management: Seniors who use digital tools maintain more consistent routines for eating, medication, and sleep.
● Renewed Sense of Connection: Even brief daily interactions make elderly users feel heard and valued — especially for those without close family nearby.
These psychological benefits are encouraging continued expansion of digital companionship programs across the country.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the success of these programs is undeniable, challenges remain.
● Technology Familiarity: Some older adults find it difficult to use new devices or interact with AI assistants.
● Emotional Dependence: Experts caution that technology should complement, not replace, human relationships.
● Privacy and Data Security: Health and behavior data must be carefully protected to prevent misuse.
● Cost and Accessibility: Although government programs subsidize many devices, private products may remain too costly for low-income seniors.
● Maintenance and Updates: Continuous technical support is essential to keep devices functional and effective.
To overcome these barriers, Korea is investing in digital literacy education for seniors and ensuring privacy regulations align with ethical caregiving practices.
Role of Families and Communities
Technology works best when supported by family and community.
● Family Engagement: Many digital tools allow family members to send voice messages or photos directly to a senior’s device, maintaining emotional connection.
● Community Centers: Senior centers across Korea offer digital training sessions where older adults learn how to use smart devices confidently.
● Volunteer Programs: Youth volunteers visit elderly homes to help set up robots or teach app usage, creating intergenerational bonding.
● Faith and Cultural Organizations: Local temples, churches, and NGOs participate in campaigns that promote emotional care through digital inclusion.
These collaborations ensure that seniors are not only using technology — they are using it meaningfully, as part of a supportive social ecosystem.
Future of Digital Companionship in Korea
The future of elder care in Korea is becoming more digital, intelligent, and empathetic.
● AI Advancements: New-generation robots will feature emotion recognition, adaptive conversation, and facial expression analysis to provide deeper companionship.
● Personalized Digital Therapists: Voice-based AI companions will offer guided meditation, music therapy, and memory exercises tailored to each user’s mood and history.
● 5G and Smart City Integration: Seniors living in “smart homes” within smart cities will benefit from real-time monitoring, emergency services, and digital companionship integrated into one system.
● Global Export Potential: Korea’s expertise in eldercare robotics is attracting international attention, with exports planned to Japan, Europe, and North America.
These advancements represent more than technological innovation — they symbolize a societal commitment to aging with dignity and connection.
Final Thoughts
Korea’s growing investment in digital companionship tools reflects its deep understanding that elder care must nurture both body and soul. By combining artificial intelligence with empathy, the country is redefining what it means to care for its aging citizens in the digital age.
● Technology with a heart — caring through connection.
● Every conversation, even digital, can bring comfort and hope.
● Korea’s innovation is turning loneliness into connection, one voice at a time.
As these tools continue to evolve, Korea is proving that technology, when guided by compassion, can bridge generations — ensuring that no one grows old alone.