Overview
A pelvic abscess is a collection of pus located in the pelvic cavity, typically resulting from infection following surgery, trauma, or complications of gynecological or gastrointestinal conditions. It is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications such as sepsis, infertility, or chronic pain.
What is Pelvic Abscess?
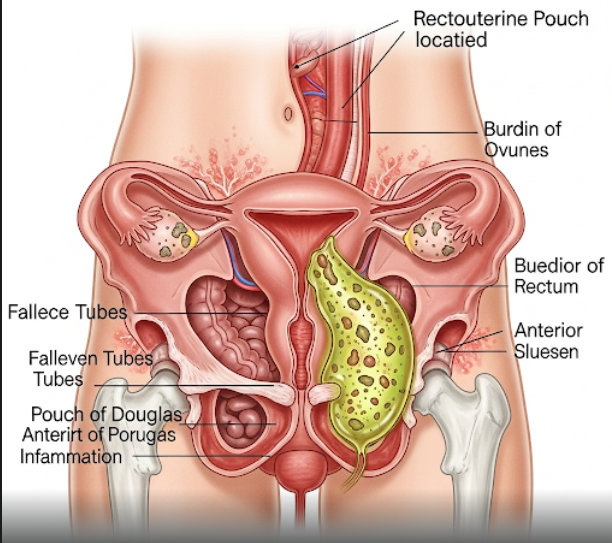
A pelvic abscess is a localized pocket of infection within the lower abdomen or pelvis. The abscess forms when the body tries to contain an infection, leading to the accumulation of pus—a thick fluid composed of white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. It may occur in both men and women but is more common in women, particularly following pelvic surgeries or gynecological infections.
Pelvic abscesses can be:
- Tubo-ovarian abscess: involving the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Postoperative abscess: forming after abdominal or pelvic surgery.
- Diverticular abscess: stemming from complications of diverticulitis.
- Appendiceal abscess: following a ruptured appendix.
Symptoms
Symptoms can vary depending on the size and location of the abscess but typically include:
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Fever and chills
- Pain during urination or bowel movements
- Vaginal discharge (in females)
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pain during intercourse
- Bloating or fullness in the lower abdomen
- Fatigue and general malaise
Causes
Pelvic abscesses can arise from various underlying issues, such as:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women
- Post-surgical infection (after C-section, hysterectomy, appendectomy)
- Ruptured appendix
- Perforated bowel or diverticulitis
- Gynecologic procedures or infections
- Intrauterine device (IUD) complications
- Trauma to pelvic organs
Bacteria involved are often polymicrobial, including E. coli, Bacteroides, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus species.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of pelvic abscess include:
- Recent abdominal or pelvic surgery
- History of PID
- Use of intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Bowel diseases like Crohn’s or diverticulitis
- Immunosuppression
- Diabetes
- Poor postoperative hygiene or wound care
Complications
If untreated or improperly managed, a pelvic abscess can lead to:
- Sepsis (life-threatening bloodstream infection)
- Rupture of the abscess, causing widespread infection
- Infertility (particularly with tubo-ovarian abscess)
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction
- Formation of fistulas
- Need for repeated surgeries or drainage procedures
Prevention
Preventative strategies for pelvic abscess include:
- Prompt treatment of infections, especially gynecological or abdominal
- Safe sex practices to avoid STIs
- Proper surgical technique and sterile precautions
- Antibiotic prophylaxis before and after surgery when indicated
- Monitoring post-operative symptoms carefully
- Timely treatment of appendicitis or diverticulitis
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options for pelvic abscesses. Leading hospitals are equipped with cutting-edge imaging, interventional radiology, and minimally invasive surgical tools to manage this condition effectively.
1. Diagnosis
- Pelvic ultrasound
- CT scan or MRI for precise localization
- Blood tests to check for infection and inflammation
2. Antibiotic Therapy
- Broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics are the first line.
- Targeted antibiotics based on culture and sensitivity results.
3. Drainage Procedures
- Image-guided percutaneous drainage (CT- or ultrasound-guided needle insertion).
- Laparoscopic drainage if image-guided techniques fail or abscess is inaccessible.
4. Surgery
- Required in severe cases or when the abscess does not respond to other treatments.
- Surgical intervention may involve abscess removal, repair of bowel perforations, or removal of infected reproductive organs.
5. Post-Treatment Monitoring
- Continuous follow-up to ensure full resolution.
- Repeat imaging to confirm the absence of residual abscesses.
- Treatment of any underlying condition to prevent recurrence.
Top Korean hospitals such as:
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Asan Medical Center
- Samsung Medical Center
- Yonsei Severance Hospital
offer comprehensive care for pelvic abscess, including multidisciplinary consultation from gastroenterology, gynecology, surgery, and infectious disease specialists.