Overview
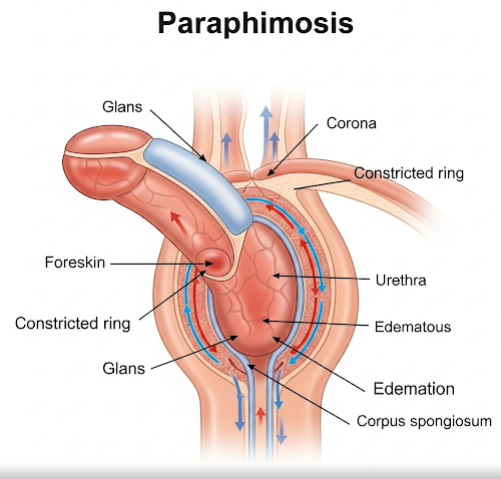
Paraphimosis is a urological emergency in which the foreskin of an uncircumcised male becomes trapped behind the head of the penis (glans) and cannot be pulled back to its normal position. This condition causes swelling, pain, and restricted blood flow to the penis. If not treated quickly, paraphimosis can lead to severe complications, including permanent damage to the penile tissue.
What is Paraphimosis?
Paraphimosis occurs when the retracted foreskin becomes stuck behind the glans penis and is unable to return to its forward position. This leads to the constriction of blood flow, causing swelling and pain. It differs from phimosis, where the foreskin cannot be retracted at all. Paraphimosis is more dangerous and requires immediate medical attention.
It most commonly occurs in uncircumcised adolescent boys or men, often due to improper handling of the foreskin during hygiene, medical procedures, or sexual activity.
Symptoms
The symptoms of paraphimosis are usually clear and immediate:
- Swelling of the penis, especially the glans
- Pain in the penile shaft or glans
- Tight, constricting band of foreskin behind the glans
- Discoloration of the glans (red or blue), indicating restricted blood flow
- Inability to pull the foreskin forward over the glans
- In severe cases: difficulty urinating
Causes
Paraphimosis can result from several triggers, including:
- Failure to reposition the foreskin after medical examinations or catheter insertion
- Improper hygiene or cleaning of the penis
- Trauma to the penis during intercourse or masturbation
- Infections causing inflammation and swelling
- Piercings or injuries
- Tight foreskin (phimosis), which predisposes the individual to paraphimosis
- Medical neglect, especially in patients who cannot communicate discomfort (e.g., elderly or disabled)
Risk Factors
Risk factors for developing paraphimosis include:
- Being uncircumcised
- Poor personal hygiene
- Young boys or elderly men who cannot manage their foreskin
- Use of urinary catheters
- Phimosis (tight foreskin)
- Recent penile procedures or examinations
- Infection or inflammation in the genital area
Complications
If paraphimosis is not treated promptly, complications can be serious and potentially permanent:
- Restricted blood flow leading to tissue necrosis (tissue death)
- Infection in the trapped foreskin or penis
- Gangrene, which may require partial or total penile amputation
- Chronic pain or erectile dysfunction
- Urinary retention due to urethral obstruction
Prevention
Most cases of paraphimosis can be prevented with proper foreskin care:
- Always return the foreskin to its original position after retraction for cleaning or catheterization
- Maintain good hygiene, especially for uncircumcised males
- Educate caregivers and healthcare workers on proper handling of the foreskin
- Avoid rough handling of the foreskin during sexual activity
- Seek medical advice for phimosis or recurring foreskin problems
- In high-risk or recurrent cases, circumcision may be recommended as a preventive option
Treatment Option in Korea
South Korea offers advanced, prompt, and effective treatment for paraphimosis. Korean hospitals, including top urology centers like Samsung Medical Center, Severance Hospital, and Asan Medical Center, are equipped to manage this emergency with the latest techniques.
1. Manual Reduction
- The most common first step.
- Doctors use lubrication and gentle compression to reduce the swelling and slide the foreskin back into place.
- Often done under local anesthesia or a numbing agent.
2. Osmotic Methods
- Involves using substances like sugar solution or cold compress to reduce swelling before manual reduction.
- This is non-invasive and often effective in mild to moderate cases.
3. Puncture Technique
- In more severe cases, small needle punctures are made in the swollen foreskin to drain trapped fluid.
- This reduces swelling and allows the foreskin to move back.
4. Dorsal Slit Surgery
- A small surgical incision on the foreskin relieves the tight constriction.
- This is usually done if manual methods fail or swelling is too severe.
5. Circumcision
- In recurrent cases or severe presentations, circumcision is the recommended permanent solution.
- Korean hospitals offer laser and minimally invasive circumcision with fast recovery.
6. Post-Treatment Monitoring & Care
- Pain relief, infection control, and daily foreskin hygiene instructions are provided.
- Follow-up appointments ensure no long-term complications occur.
Korea’s National Health Insurance (NHI) may cover a portion of the treatment costs for emergency care, and private hospitals offer premium care packages for international patients.