What it is
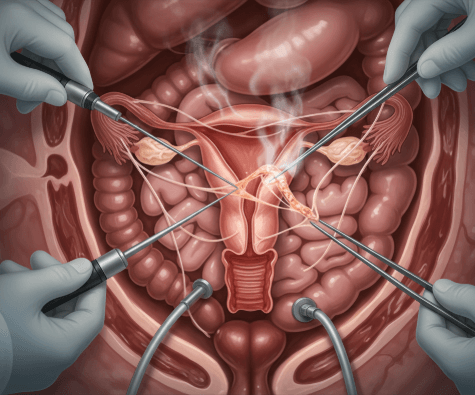
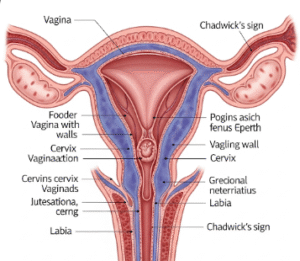
Pelvic adhesion removal, also called adhesiolysis, is a surgical procedure to separate scar tissue (adhesions) that form between pelvic organs such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, or intestines. Adhesions develop after infections, endometriosis, pelvic surgery, or trauma, and they can cause chronic pain, infertility, or bowel problems.
In Korea, pelvic adhesion removal is typically performed using laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery, allowing surgeons to cut or remove scar tissue with precision while preserving organ function and minimizing recurrence.
➡️ Key facts about pelvic adhesion removal:
- Restores normal organ movement and function
- Helps improve fertility in women with blocked fallopian tubes
- Reduces chronic pelvic pain caused by adhesions
Why it’s done
Pelvic adhesions can interfere with daily life and reproductive health, making surgical removal necessary in certain cases.
✔️ Medical reasons for adhesion removal include:
- Chronic pelvic pain due to organs sticking together
- Infertility caused by adhesions blocking the fallopian tubes or covering ovaries
- Endometriosis-related adhesions interfering with reproductive organs
- Bowel obstruction or urinary problems from extensive scar tissue
✔️ Benefits of adhesion removal:
- Relieves pelvic pain and discomfort
- Improves chances of natural conception or success with IVF
- Restores mobility of pelvic organs
- Enhances overall quality of life
Alternatives
Not all adhesions require surgery, and alternatives may be considered depending on symptoms and severity.
🔹 Medication therapy:
- Pain relievers or hormonal therapy for endometriosis-related adhesions
- May help manage symptoms but does not remove adhesions
🔹 Physical therapy:
- Pelvic physiotherapy to relieve pain and improve mobility
- Useful for mild adhesions but not a cure
🔹 Watchful waiting:
- If adhesions cause no symptoms, surgery may not be necessary
- Regular monitoring with imaging tests
🔹 Lifestyle management:
- Diet changes, stress management, and gentle exercise may reduce discomfort
Preparation
Preparation for pelvic adhesion removal ensures safety and increases effectiveness.
➡️ Medical preparation:
- Ultrasound, MRI, or hysterosalpingography (HSG) to evaluate adhesions and blockages
- Blood tests to check overall health and readiness for surgery
- Consultation about fertility goals and potential risks of recurrence
➡️ Personal preparation:
- Fasting before surgery if general anesthesia will be used
- Packing essentials for a short hospital stay (usually 1–3 days)
- Arranging family support for post-surgery recovery
➡️ Mental preparation:
- Understanding that adhesions can sometimes recur even after removal
- Preparing emotionally for the possibility of needing fertility treatments afterward
- Counseling sessions for women experiencing anxiety about surgery or infertility
How it’s done
In Korea, pelvic adhesion removal is usually performed with laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery, which provides precision and reduces risks.
✔️ Step 1 – Anesthesia
- General anesthesia administered for pain-free surgery
✔️ Step 2 – Creating access
- Small incisions made in the abdomen
- Carbon dioxide gas introduced to expand the abdomen for better visibility
✔️ Step 3 – Inserting the laparoscope
- A camera projects images of the pelvic organs onto a monitor
- Additional small incisions may be made for surgical tools
✔️ Step 4 – Cutting or removing adhesions
- Scar tissue carefully separated using scissors, electrocautery, or laser
- Surgeons work to preserve fertility and prevent organ damage
- Barrier gels or membranes may be placed to reduce recurrence of adhesions
✔️ Step 5 – Completion
- Gas released and incisions closed with sutures or surgical glue
- Patient moved to recovery room for monitoring
✔️ Duration:
- Surgery typically lasts 1–3 hours depending on severity
- Hospital stay: outpatient or 1–2 days for laparoscopic procedures, longer for open surgery
Recovery
Recovery after pelvic adhesion removal is usually fast with minimally invasive surgery.
➡️ Immediate recovery:
- Mild abdominal pain, bloating, or shoulder discomfort from gas used in surgery
- Fatigue from anesthesia
- Hospital monitoring for bleeding or infection
➡️ Physical recovery:
- Return to normal activities within 1–2 weeks for laparoscopy
- 4–6 weeks for open abdominal surgery if needed
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise until cleared by the doctor
➡️ Emotional recovery:
- Relief from chronic pelvic pain and improved fertility chances
- Counseling may help women coping with infertility or recurring adhesions
- Emotional reassurance provided through support groups or hospital counseling services
➡️ Key recommendations:
- Adequate rest and proper wound care
- Balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
- Gentle walking to improve circulation and reduce risks of clots
- Attending follow-up visits to monitor healing and recurrence prevention
Treatment option in Korea
Korea is recognized for its world-class gynecological surgery and fertility-preserving care, making it a leading destination for pelvic adhesion removal.
✔️ Hospital facilities:
- Equipped with high-definition laparoscopic and robotic surgery systems
- Specialized women’s hospitals with fertility and endometriosis treatment programs
- Advanced imaging for accurate diagnosis and surgical planning
✔️ Medical expertise:
- Skilled surgeons with high success rates in adhesion removal
- Focus on preserving fertility and organ function
- Use of anti-adhesion agents and cutting-edge surgical tools to reduce recurrence
✔️ Postoperative care:
- Holistic recovery programs including physical therapy and pain management
- Fertility counseling for women planning pregnancy
- Emotional support services for women coping with infertility or chronic pain
✔️ Cultural aspect:
- Korean healthcare places great emphasis on fertility preservation and long-term quality of life
- Families often provide strong support during recovery
- Integration of traditional Korean medicine and nutrition for enhanced healing
➡️ Highlight: Pelvic adhesion removal in Korea provides advanced minimally invasive surgery, fertility-focused outcomes, and comprehensive recovery support, ensuring women receive safe, effective, and holistic treatment.