Overview
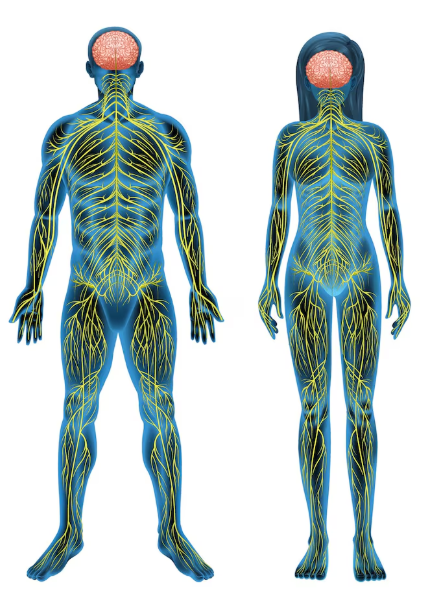
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is part of the autonomic nervous system that controls involuntary functions like heart rate, blood pressure, and stress responses. Dysfunction in the SNS can cause a wide range of problems including poor circulation, abnormal sweating, irregular heartbeat, digestive issues, and chronic pain. In Korea, specialized neurology and autonomic disorder clinics provide advanced diagnostic testing and personalized treatments for SNS dysfunction.
What is Sympathetic Nervous System Dysfunction?
Sympathetic nervous system dysfunction refers to an imbalance or malfunction in the nerves responsible for the “fight or flight” response. This can manifest as either overactivity or underactivity of the SNS and is often associated with autonomic nervous system disorders such as:
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
- Autonomic Neuropathy
- Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)
- Pure Autonomic Failure
This condition may be primary (idiopathic) or secondary to other diseases, trauma, or medication side effects.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary based on whether the dysfunction is due to hyperactivity or hypoactivity. Common signs include:
- Abnormal heart rate or blood pressure
- Dizziness or fainting (especially when standing)
- Cold hands and feet
- Chronic pain (especially in limbs)
- Excessive or reduced sweating
- Digestive problems (e.g., nausea, constipation)
- Blurred vision
- Anxiety or panic attacks
- Temperature regulation issues
Causes
- Diabetes mellitus (autonomic neuropathy)
- Spinal cord injury or trauma
- Autoimmune diseases
- Chronic stress or PTSD
- Parkinson’s disease or Multiple System Atrophy
- Surgical nerve damage
- Certain medications (e.g., beta-blockers, antidepressants)
- Infections (e.g., COVID-19-related dysautonomia)
Risk Factors
- Family history of autonomic or neurological disorders
- Chronic illness (especially diabetes)
- History of nervous system injury
- Autoimmune conditions
- Long-term alcohol abuse
- Aging (neurodegeneration)
- Exposure to neurotoxic agents
Complications
If left untreated, sympathetic nervous system dysfunction may lead to:
- Cardiovascular instability (e.g., fainting, arrhythmias)
- Severe functional impairment
- Increased risk of injury from falls
- Chronic pain syndromes
- Organ dysfunction
- Reduced quality of life
Prevention
While not all cases are preventable, some measures may reduce risk or delay progression:
- Control blood sugar levels (for diabetics)
- Manage autoimmune conditions effectively
- Limit alcohol and drug abuse
- Minimize stress through mindfulness and therapy
- Avoid nerve-damaging toxins or medications when possible
- Regular medical check-ups for early detection
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is equipped with cutting-edge facilities for diagnosing and treating autonomic disorders, including SNS dysfunction.
Diagnosis
- Autonomic Function Tests (AFT)
- Tilt Table Test (for orthostatic intolerance)
- Heart Rate Variability Analysis
- Thermoregulatory Sweat Testing
- QSART (Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test)
- MRI or CT Scans (to rule out central nervous system damage)
- Electromyography (EMG) & Nerve Conduction Studies
Medical Treatment
- Medications:
- Beta-blockers or alpha-agonists (to regulate blood pressure and heart rate)
- Neuropathic pain medications (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin)
- Antidepressants or anxiolytics
- GI motility drugs for digestive symptoms
- IV Fluids and Salt Tablets (for orthostatic hypotension)
- Immunosuppressive therapy (for autoimmune causes)
Lifestyle and Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy and gradual reconditioning
- Compression garments to prevent blood pooling
- Adequate hydration and high-salt diet (if advised)
- Stress management techniques (e.g., biofeedback, CBT)
- Acupuncture and traditional Korean medicine (in integrative clinics)
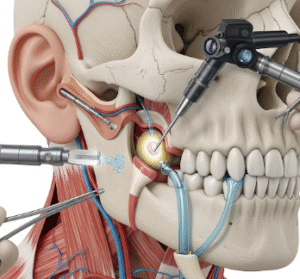
Surgical and Interventional Options
- Sympathectomy: In rare and severe cases like CRPS, surgical interruption of sympathetic nerves may be considered.
- Implantable devices (e.g., pacemakers) for severe cardiac dysautonomia