Overview
Sprains and strains are common soft tissue injuries that affect muscles, ligaments, and tendons, typically resulting from sudden movements, overuse, or accidents. These injuries are frequently seen in sports, physical labor, and daily activities. In Korea, with growing awareness of fitness and sports participation, such injuries are increasingly being diagnosed and treated with a mix of conservative therapy and advanced rehabilitation techniques.
What are Sprains and Strains?
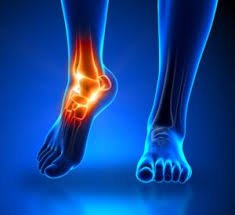
- Sprains involve the stretching or tearing of ligaments, which are the bands of tissue connecting bones at a joint. Common areas include the ankle, knee, and wrist.
- Strains affect muscles or tendons (which connect muscles to bones), and often occur in the back, hamstring, or neck.
While they share similar symptoms, the tissues involved differ. Both conditions can range from mild overstretching to complete tears, requiring different levels of care.
Symptoms
Sprain Symptoms:
- Pain around the affected joint
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited movement or instability
- A “pop” sound at the time of injury (in severe cases)
Strain Symptoms:
- Muscle pain and weakness
- Swelling or cramping
- Limited motion
- Muscle spasms
Causes
- Sudden twisting or impact (sports injuries, falls, accidents)
- Lifting heavy objects improperly
- Overuse of a specific joint or muscle
- Poor flexibility or lack of conditioning
- Inadequate warm-up before exercise
Risk Factors
- Engaging in high-impact sports (soccer, basketball, skiing)
- Fatigue or poor conditioning
- Slippery or uneven surfaces
- Wearing inappropriate footwear
- Age-related muscle and ligament weakening
- Previous injuries (higher risk of recurrence)
Complications
- Chronic pain or instability
- Joint stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Tendonitis or bursitis from improper healing
- Muscle atrophy due to prolonged inactivity
- Risk of re-injury if rehabilitation is incomplete
Prevention
- Warm up properly before physical activity
- Use proper lifting techniques
- Wear supportive footwear
- Avoid overtraining and take rest breaks
- Use braces or supports during high-risk activities
- Strengthen muscles around joints through regular exercise
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea has a well-established orthopedic and rehabilitation system, offering both traditional and modern treatments for sprains and strains.
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination
- Range of motion tests
- Imaging (X-ray to rule out fractures, MRI for ligament/muscle tears)
Initial Treatment (R.I.C.E method):
- Rest: Avoid activity that worsens symptoms
- Ice: Apply cold packs 20 minutes at a time
- Compression: Use elastic bandages to reduce swelling
- Elevation: Keep the injured area above heart level
Medical Treatments:
- Pain relievers: NSAIDs like ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Physical therapy: Tailored exercises to restore strength and mobility
- Manual therapy or chiropractic care: For spinal and back strains
- Ultrasound or electrical stimulation therapy: For muscle recovery
- Corticosteroid injections: For persistent inflammation (used cautiously)
- Surgery: Rare but may be required for complete ligament or tendon tears
Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM) Options:
- Acupuncture and cupping therapy
- Chuna manual therapy (Korean chiropractic technique)
- Herbal medicine for inflammation and pain relief