Overview
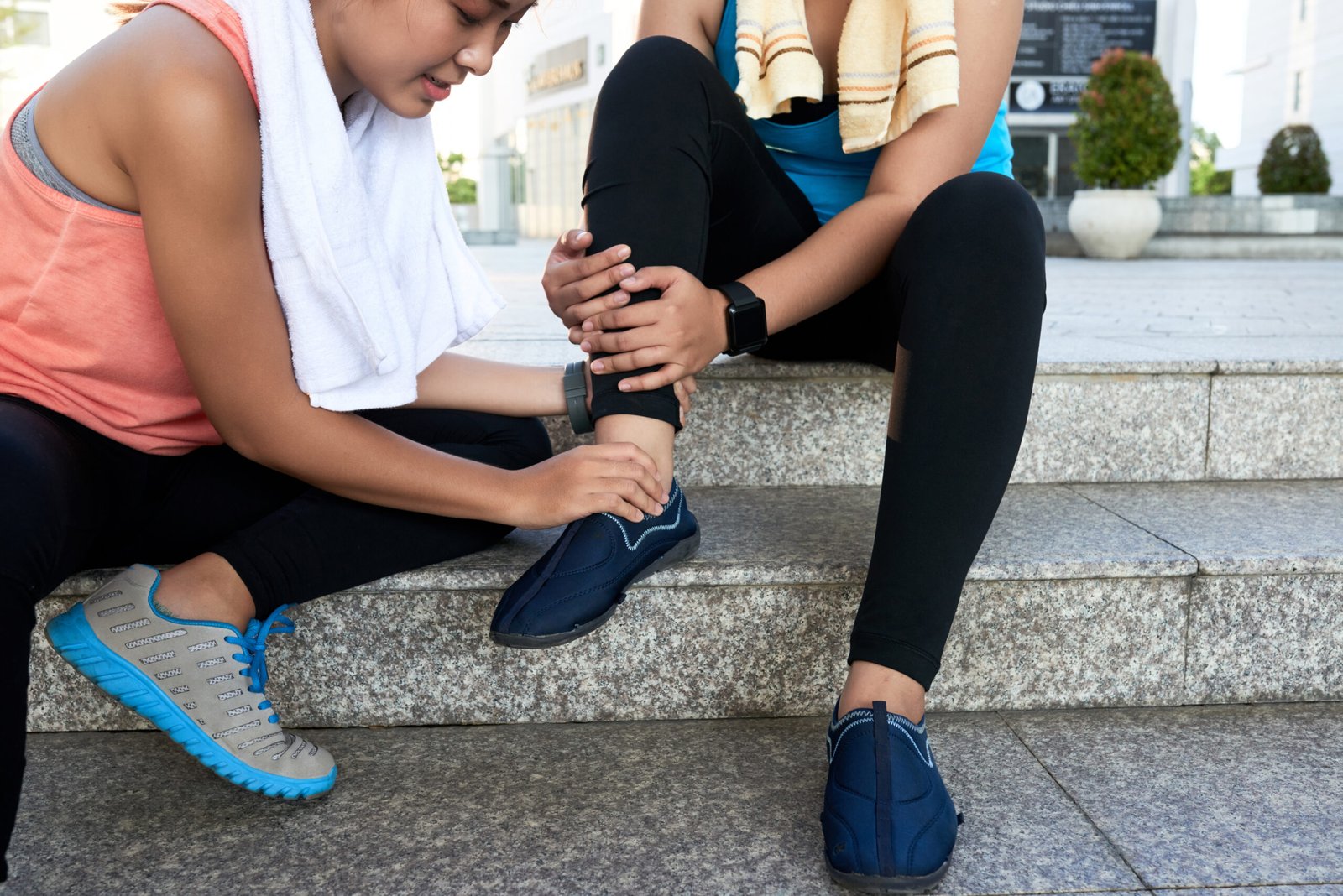
A sprained ankle is one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries, occurring when the ligaments that support the ankle are stretched or torn due to sudden twisting or rolling motions. It often causes pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. In Korea, sprained ankles are effectively managed with modern diagnostic tools and treatment protocols in hospitals, orthopedic clinics, and rehabilitation centers.
What is a Sprained Ankle?
A sprained ankle involves damage to one or more ligaments around the ankle joint, typically the lateral ligaments. The injury can range from mild ligament stretching to a complete tear. Proper treatment and rehabilitation are crucial to restore ankle stability and prevent chronic problems.
Symptoms
- Pain around the ankle, especially when bearing weight
- Swelling and bruising
- Tenderness on the affected ligaments
- Limited range of motion
- Instability or a feeling of the ankle “giving way”
- Difficulty walking or standing
Causes
- Twisting or rolling the ankle during sports or walking on uneven surfaces
- Sudden impact or fall
- Improper footwear
- Weak ankle muscles or previous injuries
Risk Factors
- Participation in sports involving jumping, running, or sudden direction changes
- Previous ankle sprains
- Poor physical conditioning or muscle weakness
- Walking or running on uneven or slippery surfaces
- Wearing inappropriate shoes
Complications
- Chronic ankle instability
- Recurring sprains
- Tendon injuries
- Arthritis in the ankle joint
- Persistent pain and swelling
Prevention
- Wear proper, supportive footwear
- Strengthen ankle muscles with exercises
- Warm-up and stretch before physical activity
- Avoid walking on uneven or slippery surfaces when possible
- Use ankle braces or taping during high-risk activities
Treatment Options in Korea
- Immediate Care
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE) method applied as soon as possible
- Immobilization with ankle braces or splints, available at pharmacies and clinics
- Over-the-counter pain medications such as NSAIDs
- Medical Evaluation
- Orthopedic assessment to determine injury severity
- Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI to exclude fractures or severe ligament tears
- Physical Therapy
- Personalized rehabilitation programs at Korean physiotherapy centers
- Exercises to restore strength, flexibility, and balance
- Advanced modalities including ultrasound therapy and manual therapy
- Surgical Intervention
- Considered for severe ligament ruptures or chronic instability
- Arthroscopic or open ligament repair performed in major Korean hospitals like Samsung Medical Center and Seoul National University Hospital
- Post-surgical rehabilitation to regain function
- Follow-up and Prevention
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor healing
- Education on ankle care and injury prevention
- Gradual return to sports with protective support