Surgical removal of benign oral cavity cysts for comfort and cosmetic care
What it is
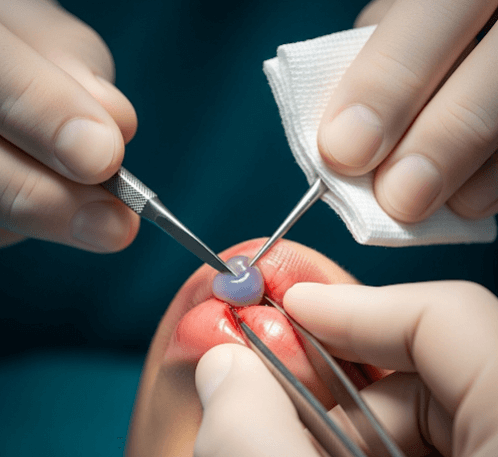
A mucous cyst (mucocele) is a benign, fluid-filled swelling in the mouth caused by the blockage or rupture of a salivary gland duct. Mucoceles most often appear on the inner surface of the lips, but may also occur on the tongue, palate, or floor of the mouth.
They typically look like soft, bluish, dome-shaped lesions that may vary in size. While painless, they can sometimes interfere with chewing, speaking, or cause discomfort when accidentally bitten.
Excision (surgical removal) is the standard treatment for mucoceles that are persistent, large, or recurrent. In Korea, excision procedures are performed by oral surgeons, dermatologists, or ENT specialists, often in outpatient settings using advanced, minimally invasive techniques.
Why it’s done
Mucous cyst excision is recommended for several important reasons:
✔ Definitive removal – Prevents recurrence by eliminating the cyst and its associated gland.
✔ Symptom relief – Resolves discomfort from chewing, irritation, or swelling.
✔ Cosmetic improvement – Restores normal appearance of the lips and mouth.
✔ Functional restoration – Prevents interference with speaking or eating.
✔ Rule out other conditions – Ensures the lesion is not mistaken for a tumor or other oral pathology.
Alternatives
While excision is the gold standard, alternatives may be considered in select cases.
→ Observation – Small mucoceles sometimes rupture and heal on their own.
→ Cryotherapy – Freezing the cyst with liquid nitrogen; less commonly used.
→ Laser ablation – Vaporizes the cyst with CO₂ or diode laser; widely used in Korean clinics.
→ Marsupialization – Opening the cyst and suturing edges to allow continuous drainage; used for larger mucoceles, especially on the floor of the mouth (ranula).
→ Steroid injections – Rarely used, as effect is temporary.
In Korea, laser excision is a popular alternative due to faster healing and minimal scarring.
Preparation
Preparation for mucocele excision ensures safety and good outcomes.
➤ Clinical evaluation – Oral examination confirms diagnosis.
➤ Medical history – Review of previous cyst episodes, medications, and bleeding risk.
➤ Imaging/biopsy – In uncertain cases, ultrasound or biopsy may be performed.
➤ Pre-procedure instructions – Patients may be asked to avoid blood-thinning medications.
➤ Counseling – Doctors explain the procedure, healing time, and recurrence risk.
How it’s done
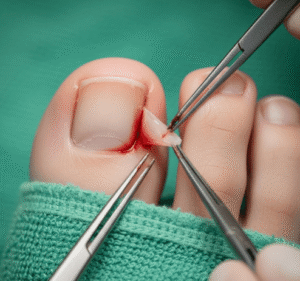
Excision is typically a short outpatient procedure.
➔ Anesthesia – Local anesthetic is injected around the lesion.
➔ Incision – A small cut is made to expose the cyst.
➔ Cyst removal – The mucocele and the affected salivary gland tissue are carefully excised to prevent recurrence.
➔ Closure – The wound is closed with absorbable sutures or left to heal naturally, depending on size and location.
➔ Laser excision (in Korea) – Many clinics use CO₂ or diode lasers for bloodless removal and reduced healing time.
The procedure usually takes 15–30 minutes.
Recovery
Recovery after mucocele excision is quick and well tolerated.
→ Mild swelling, soreness, or minor bleeding may occur for a few days.
→ Soft diet and avoidance of spicy/acidic foods are recommended during healing.
→ Stitches dissolve in 1–2 weeks if used.
→ Complete healing occurs in 2–3 weeks, with minimal scarring.
→ Follow-up visits ensure proper healing and monitor for recurrence.
Complications
While safe, mucous cyst excision has potential risks.
✔ Recurrence – If the entire cyst and gland are not removed.
✔ Infection – Rare with proper oral hygiene.
✔ Bleeding – Minimal and usually self-limited.
✔ Scarring – Uncommon but possible with larger lesions.
✔ Nerve irritation – Rare, but numbness may occur if nerves are close to the lesion.
In Korea, use of laser excision and microsurgical techniques minimizes these risks.
Treatment options in Korea
Korea offers advanced treatment approaches for mucoceles, combining medical safety with cosmetic excellence.
➤ Laser excision clinics – Widely available in Seoul, Busan, and Incheon, offering CO₂ or diode laser removal with faster recovery.
➤ Multidisciplinary expertise – Oral surgeons, dermatologists, and ENT specialists collaborate for precise treatment.
➤ Cosmetic outcomes – Procedures are tailored to minimize scarring and maintain lip/mouth aesthetics.
➤ Enhanced aftercare – Clinics provide antiseptic rinses, pain relief, and wound care instructions.
➤ Pediatric care – Specialized techniques ensure comfort and safety for children with mucoceles.
➤ International services – Korean hospitals offer bilingual consultations, customized scheduling, and follow-up care for foreign patients.
➤ Research and innovation – Korean specialists actively study minimally invasive and regenerative therapies for oral lesions, keeping practices up to date.
By choosing mucocele excision in Korea, patients benefit from expert surgical precision, advanced technology, and excellent cosmetic outcomes, ensuring both functional relief and restored confidence.