What It Is
Umbilical hernia repair is a surgical procedure to correct a bulge or protrusion around the belly button caused by abdominal tissue or intestines pushing through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. While it is primarily a medical procedure, many patients choose to combine it with cosmetic abdominal surgery, such as a tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) or liposuction, for both functional and aesthetic improvement.
In Korea, surgeons often perform umbilical hernia repair as part of cosmetic body contouring, ensuring not only the restoration of abdominal wall strength but also a smoother, more natural-looking belly button and abdominal profile.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo umbilical hernia repair (with cosmetic adjunct) because:
- They experience pain, bulging, or discomfort in the navel area.
- The hernia is noticeable and affects aesthetic appearance.
- They want to correct the hernia while also undergoing tummy tuck or body contouring.
- They want a long-term solution that improves both health and body shape.
Good candidates include:
- Adults with small to moderate umbilical hernias.
- Patients with abdominal wall weakness after pregnancy or weight changes.
- Those planning body contouring procedures for cosmetic enhancement.
Alternatives
- Watchful waiting: In very small, asymptomatic hernias.
- Support garments: May provide temporary relief but do not repair the hernia.
- Standalone hernia repair: Without cosmetic procedures, if aesthetics are not a concern.
Preparation
Before umbilical hernia repair in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo physical examination and imaging (ultrasound or CT scan).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and supplements.
- Discuss whether the procedure will be combined with tummy tuck, liposuction, or abdominal wall tightening.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia or local with sedation depending on complexity.
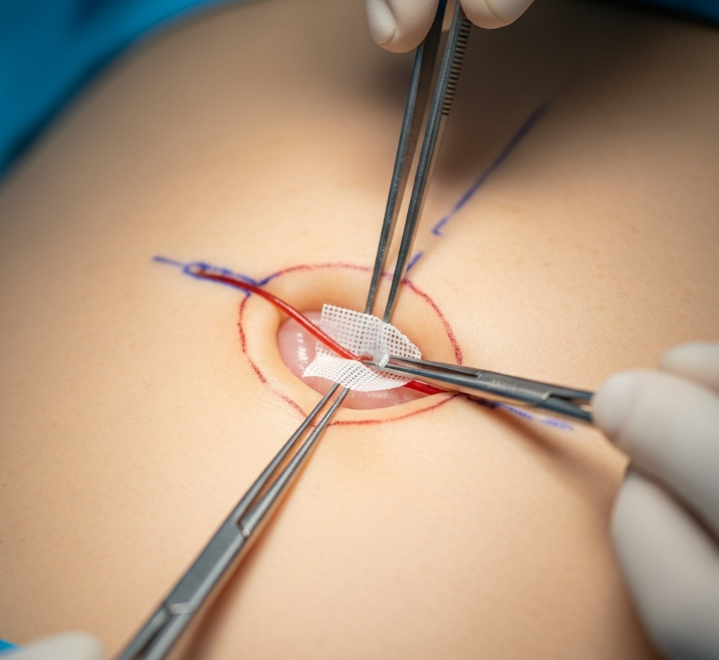
- Incision: Made near the belly button, often hidden in natural creases.
- Hernia repair: The hernia sac is reduced, and the abdominal wall is reinforced with sutures or mesh.
- Cosmetic adjunct: If combined with abdominoplasty, excess skin and fat are removed, and the belly button is reshaped.
- Duration: 1–3 hours depending on whether additional cosmetic procedures are performed.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, soreness, and mild bruising; compression garment worn if combined with body contouring.
- Hospital stay: Same-day discharge or 1–2 nights for complex cases.
- Return to activities: Light duties in 1–2 weeks; strenuous exercise avoided for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Stronger abdominal wall and improved belly button contour within 2–3 months.
Possible Complications
- Recurrence of hernia (rare with proper repair).
- Infection or delayed wound healing.
- Seroma (fluid buildup) or hematoma.
- Visible scarring, though minimized with Korean techniques.
- Rare risks: bowel injury or mesh-related complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use physical examination, ultrasound, or CT scans to evaluate the size and severity of the hernia before planning surgery.
Medical Treatments
- Observation for very small, asymptomatic hernias.
- Supportive garments for temporary relief.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Primary suture repair for small hernias.
- Mesh reinforcement for larger or recurrent hernias.
- Umbilical hernia repair with tummy tuck for combined functional and cosmetic results.
- Repair with liposuction or abdominal plication for improved body contour.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Compression garments for abdominal support after surgery.
- Scar care with silicone sheets or laser if combined with abdominoplasty.
- Long-term monitoring to prevent recurrence.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s combined reconstructive and cosmetic expertise, advanced mesh technology, and tailored aftercare services.